Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Treatment with azithromycin + conventional therapies was more efficacious than clarithromycin+ conventional therapies in patients diagnosed with chronic rhinosinusitis.
For management of chronic rhinosinusitis in adults, a four-week course of conventional therapies and 500 mg azithromycin daily exhibited better resolution of symptoms when compared to the combination of conventional therapies and 1,000 mg clarithromycin daily, as elucidated from a randomized controlled trial published in the Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences. Mehdi Askari et al. aimed to compare the efficacy of macrolides (clarithromycin and azithromycin) combined with conventional interventions to treat chronic rhinosinusitis.
In this single-blind study, 90 (out of 102) subjects were recruited and randomly divided into two groups. Subjects in the clarithromycin group were given 500 mg clarithromycin tablets 2 times a day for 4 weeks in addition to the conventional therapies (steam inhalation, guaifenesin syrup, fluticasone and oxymetazoline spray, betamethasone injection, and nasal irrigation). Subjects in the other group were administered 500 mg azithromycin tablets daily for 4 weeks.
Assessment of the patients’ symptoms was done before and after the intervention. Utilizing Lund-Mackay (LM) scoring system, staging of chronic rhinosinusitis was done based on computed tomography scan results. Analysis of data was done utilizing SPSS software. P<0.05 was deemed statistically significant. In terms of sex and age, subjects in both groups were similar. Compared to the clarithromycin group, the azithromycin group exhibited better complete resolution of symptoms, as shown in Table 1:
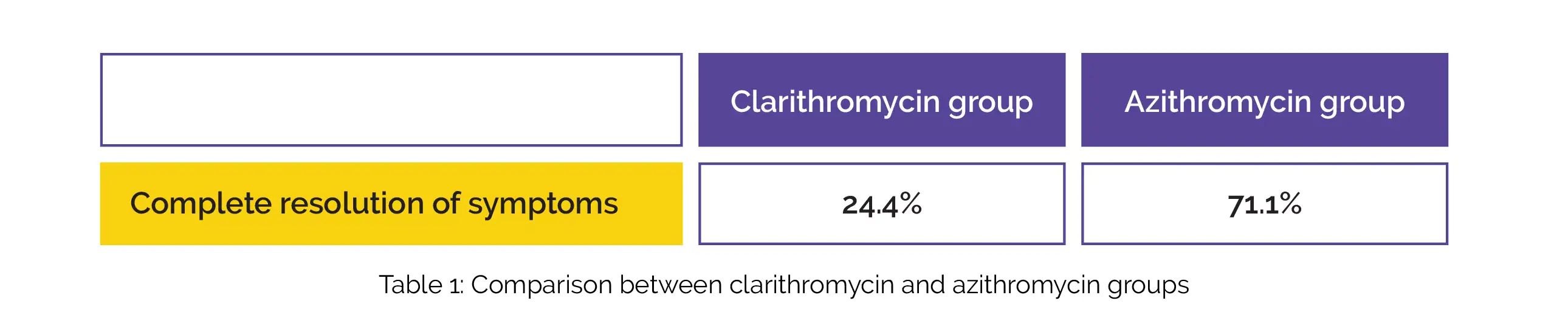
LM scores at baseline did not differ substantially between the groups. The LM scores decreased remarkably in both groups post-intervention. However, the azithromycin group exhibited remarkably greater change. Hence, the novel combination therapy (azithromycin plus conventional therapies) appear to be valuable in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis.
Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences
Introducing a Novel Combination Therapy with Macrolides for the Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Mehdi Askari et al.
Comments (0)