Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Patients with acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis and orbitocranial involvement exhibit a high survival rate when treated with azole antifungal.
In a research conducted by Tessler et al., treatment with azole in cases of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis complicated by orbitocranial fungal infection (OCFI) was associated with a low mortality rate. The study sought to provide practical, real-world data regarding the results of azole treatment and the significance of surgery in the current management of rhinosinusitis with complications involving OCFI.
Retrospective data collection was conducted through chart reviews at 4 participating centres and a systematic literature review. The study group comprised 125 OCFI patients who were treated with azole antifungals, while the control group, consisted of 153 OCFI patients who were treated with other antifungal agents. Staging based on imaging was employed to assess the degree of cranial and orbital involvement, and the extent of surgical resection was classified to facilitate inter-group comparison.
In the cohort of patients exhibiting cranial extension of OCFI, surgical intervention was carried out in 23% of individuals in the azole-treated group and 18% in the control group. However, resection of meninges and brain occurred exclusively in the control group, accounting for 11% of patients, and was never performed in the azole antifungal group. Surgical intervention became necessary for orbital involvement in 26% of cases treated with azole and 39% of cases in the control group.
Even though azole-treated patients experienced more severe cranial involvement, their mortality rate was significantly lower than that of the control group as depicted in Table 1.
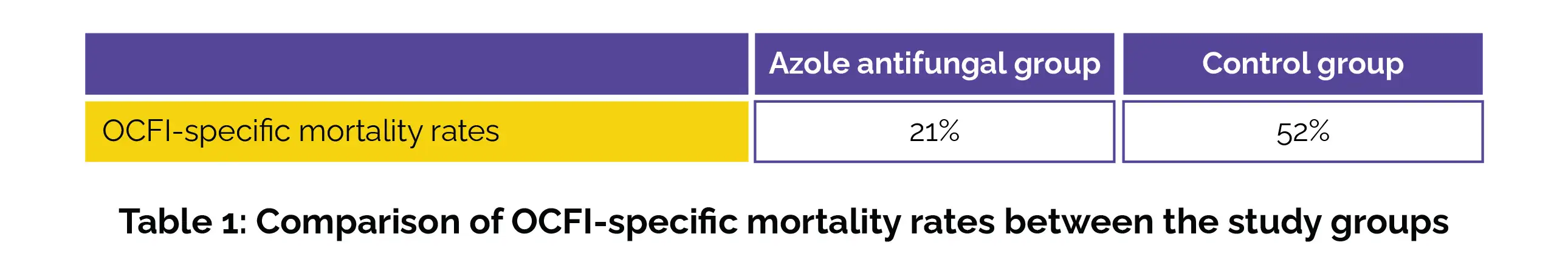
A similar pattern, though not statistically valid, was observed for the extent of orbital disease and surgery. Despite employing a less aggressive surgical approach for cranial involvement, OCFI patients undergoing azole treatment exhibited a higher survival rate. This discovery implies that adopting a more conservative surgical approach alongside azole treatment could potentially enhance morbidity outcomes. A similar pattern is also becoming evident in cases involving orbital participation.
Rhinology
Impact of azole antifungal treatment on outcome in acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis with orbitocranial involvement: a surgical perspective
I. Tessler et al.
Comments (0)