Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


For eye surgery, the cold saline solution (0.9% NaCl) has comparable efficacy and safety when compared to topical ophthalmic proparacaine.
According to the findings of a recent study, the cold saline solution is a cost-effective and easily accessible methodology, with similar safety and efficacy profile, in comparison with topical ophthalmic proparacaine to maintain topical anesthesia of people undergoing phacoemulsification surgery due to cataracts. In this double-blinded randomized clinical trial, the researchers aimed to explore the safety and efficacy of cold saline solution vs. ophthalmic proparacaine in phacoemulsification.
Participants were divided into (i) Group A (cold saline group): Incorporated 86 eyes (n=86) that were treated with topical anesthesia of cold saline solution only (ii) Group B (proparacaine group): Incorporated 84 eyes (n=84) that were treated with topical ophthalmic proparacaine (room temperature) anesthesia alone. Pain evaluation was performed utilizing a visual analog scale (VAS). Using Surgeon Questionnaire Scale (SQS), the doctor scored surgical experience in 3 parameters. Based on questions regarding comfort and ease during operation, each parameter was ranked from 1 to 3.
For the study groups, the mean VAS scores and mean scores of SQS are shown in Table 1:
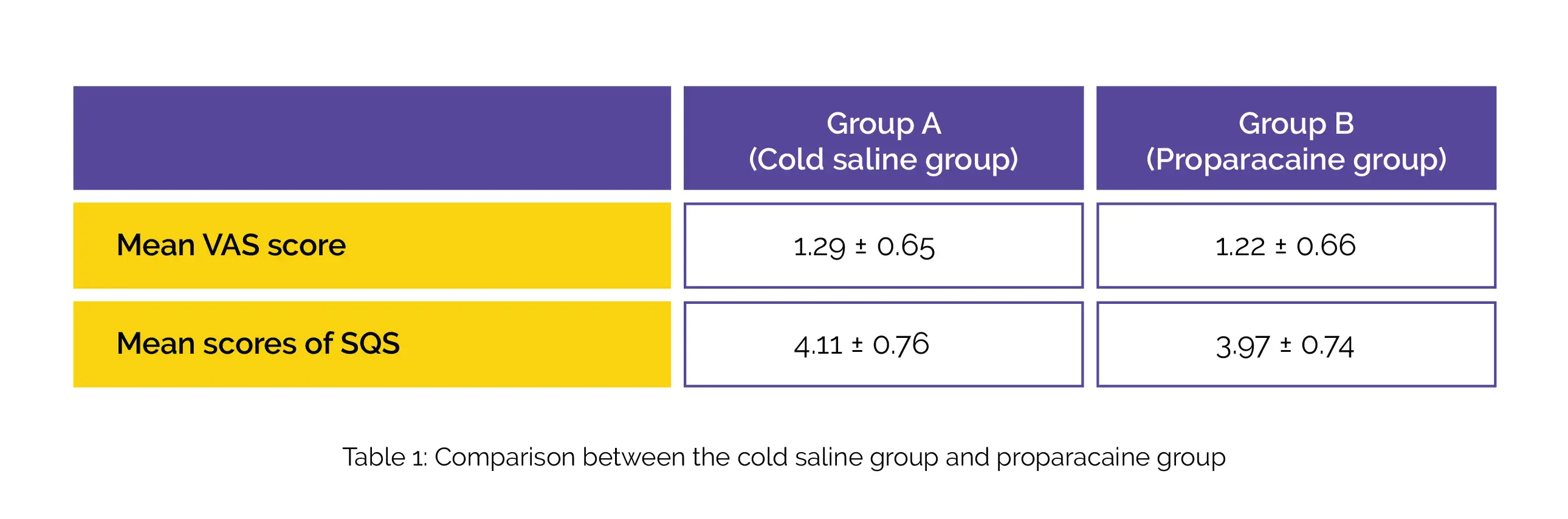
In the proparacaine group, 10 participants reported corneal epitheliopathy in the postoperative period. The absence of toxic or allergic effects offered a significant advantage for cold saline application.
Hence, the cold saline solution appears to be a promising substitute to topical ophthalmic proparacaine for the maintenance of topical anesthesia.
Indian Journal Of Ophthalmology
A double-blinded randomized clinical trial for pain perception: The efficacy and safety of topical cold saline solution anesthesia in phacoemulsification
Mehmet Demir et al.
Comments (0)