Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In coronavirus-infected people, the combination of rSIFN-co and antiviral drugs led to remarkable improvements in recovery when compared to the combination of interferon-alpha and antiviral drugs.
Compared to treatment with interferon-alpha + antiviral drugs, the new genetically engineered rSIFN-co (recombinant super-compound interferon) + antiviral drugs (lopinavir–ritonavir or umifenovir) was linked with a shorter time of clinical improvement in people with moderate-to-severe COVID-19, according to the outcomes of a study published in Annals of Medicine.
Chuan Li et al. undertook this multicenter randomized trial to determine the effectiveness of rSIFN-co (12 IU, twice daily) vs. traditional interferon-alpha (5 million IU, twice daily) added to baseline antiviral drugs to manage coronavirus disease.
Overall, 94 adult participants hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection were given either rSIFN-co nebulization (n=46) or interferon-alpha nebulization (n=48) added to baseline antiviral drugs for not more than 28 days. Time to clinical improvement was the major outcome while time to radiological improvement, time to virus nucleic acid negative conversion, and clinical improvement rate on day 28 were the secondary outcomes.
rSIFN-co plus antiviral agents shortened the time to virus nucleic acid negative conversion, clinical and radiological improvement. Furthermore, the overall clinical improvement rate on day 28 was also substantially greater in the rSIFN-co group when compared to the traditional interferon-alpha group, as shown in Table 1:
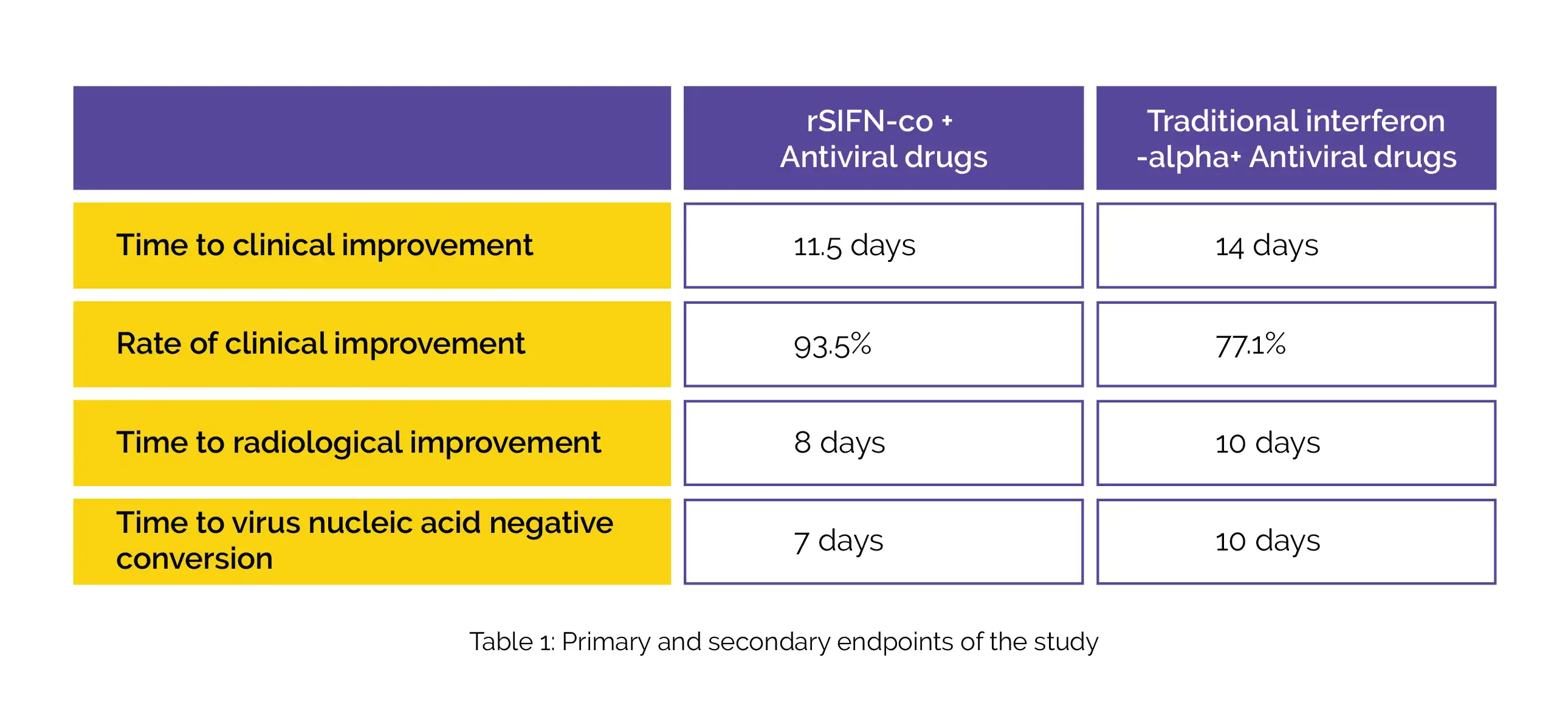
Adverse effects were balanced. No deaths were reported. For SARS-CoV-2 management, the genetically engineered interferon-alpha showed superior efficacy over traditional interferon-alpha when combined with antiviral drugs. rSIFN-co therapy alone or in combination with other antiviral therapy is worth to be further investigated.
Annals of Medicine
Effect of a genetically engineered interferon-alpha versus traditional interferon-alpha in the treatment of moderate-to-severe COVID-19: a randomised clinical trial
Chuan Li et al.
Comments (0)