Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


When used for third molar surgery, Dexmedetomidine can achieve similar sedation effectiveness as Midazolam.
A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials depicted that Dexmedetomidine could be a viable substitute for Midazolam in sedating patients undergoing third molar surgery. Wang et al. conducted this study to investigate the impact of Dexmedetomidine compared to Midazolam in dental surgery.
To search randomized controlled trials that evaluated the comparative impact of Dexmedetomidine and Midazolam in third molar surgery, databases including the Cochrane Library, EBSCO, Web of Science, Embase, and PubMed were investigated. The meta-analysis was conducted employing a random-effect model.
Incorporating a total of four randomized controlled trials, the findings revealed that when compared to Midazolam for molar surgery, the utilization of Dexmedetomidine resulted in similar oxygen saturation, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and occurrences of nausea and vomiting (Table 1).
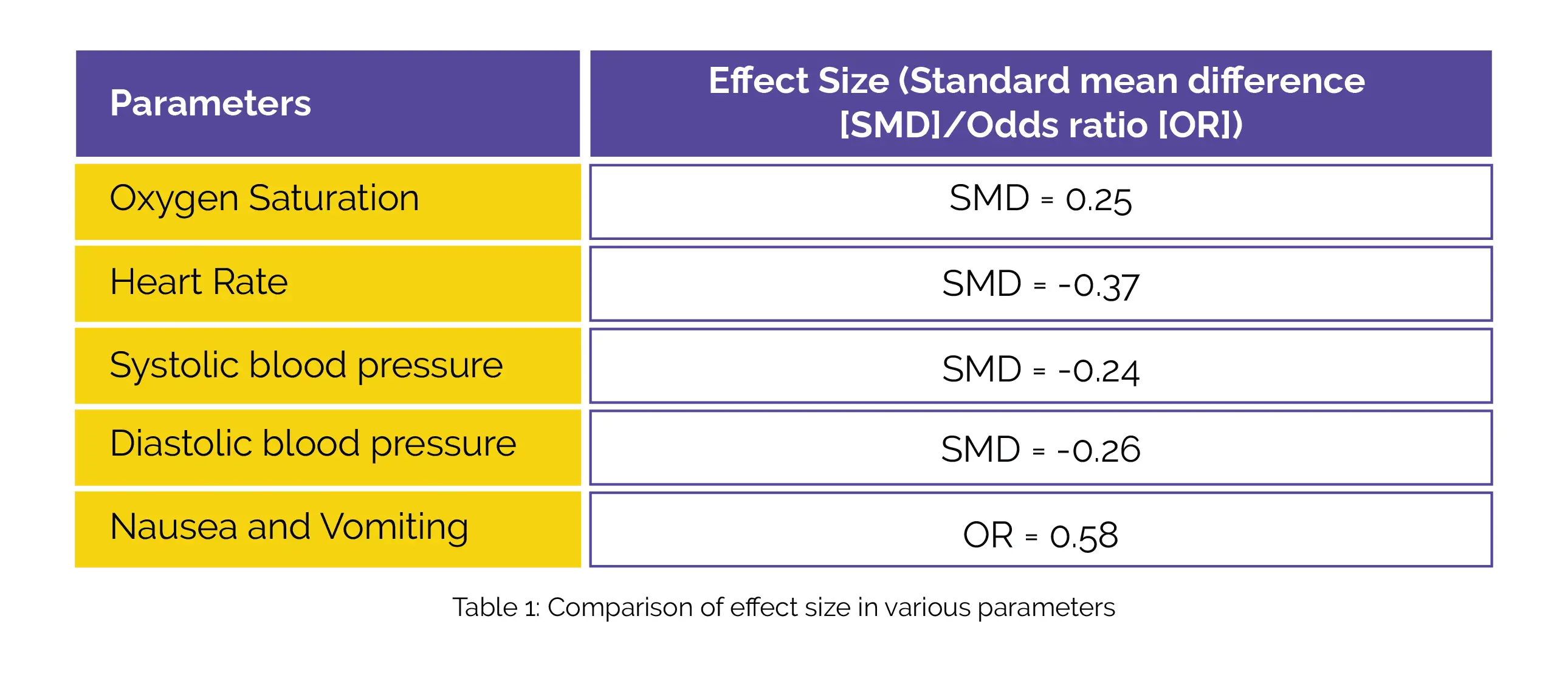
Therefore, Dexmedetomidine could be a promising substitute for Midazolam in achieving sedation during third molar surgery.
Medicine
Comparison of Dexmedetomidine with Midazolam for third molar surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ling Wang et al.
Comments (0)