Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Injection of triamcinolone is an effective therapeutic choice to add to education and advice for hip osteoarthritis patients.
A single-blind, parallel-group, three-arm, randomized controlled trial depicted that in comparison with advice and education alone in hip osteoarthritis patients, a single ultrasound-guided hip injection of triamcinolone given along with education and advice resulted in betterment in function and reduction in pain over a six-month period. Zoe Paskins et al. aimed to examine the clinical efficacy of the addition of hip injection of corticosteroid and local anaesthetic to education and advice.
In Hip Injection Trial (HIT), 199 adults ( ≥40 yrs of age, 113 women) suffering from hip osteoarthritis (at least moderate pain) were randomly divided into three groups: (I) Advice and education group (n=67), (II) Advice and education + injection of triamcinolone and lidocaine group (n=66) who were given 40 mg triamcinolone acetonide and 4 mL 1% lidocaine hydrochloride, and (III) Advice and education + injection of lidocaine group (n=66) who were given 5 ml 1% lidocaine.
Self-reported hip pain intensity (Numerical Rating Scale, NRS) at 2 weeks and at 2, 4, and 6 months was the major endpoint ascertained over 6 months. Average weighted follow-up rate of participants was 93%. Compared to advice and education alone, ultrasound-triamcinolone-lidocaine + advice and education resulted in greater mean improvement in hip pain intensity over 6 months (mean difference = -1.43, standardized mean difference = -0.55), as shown in Figure 1:
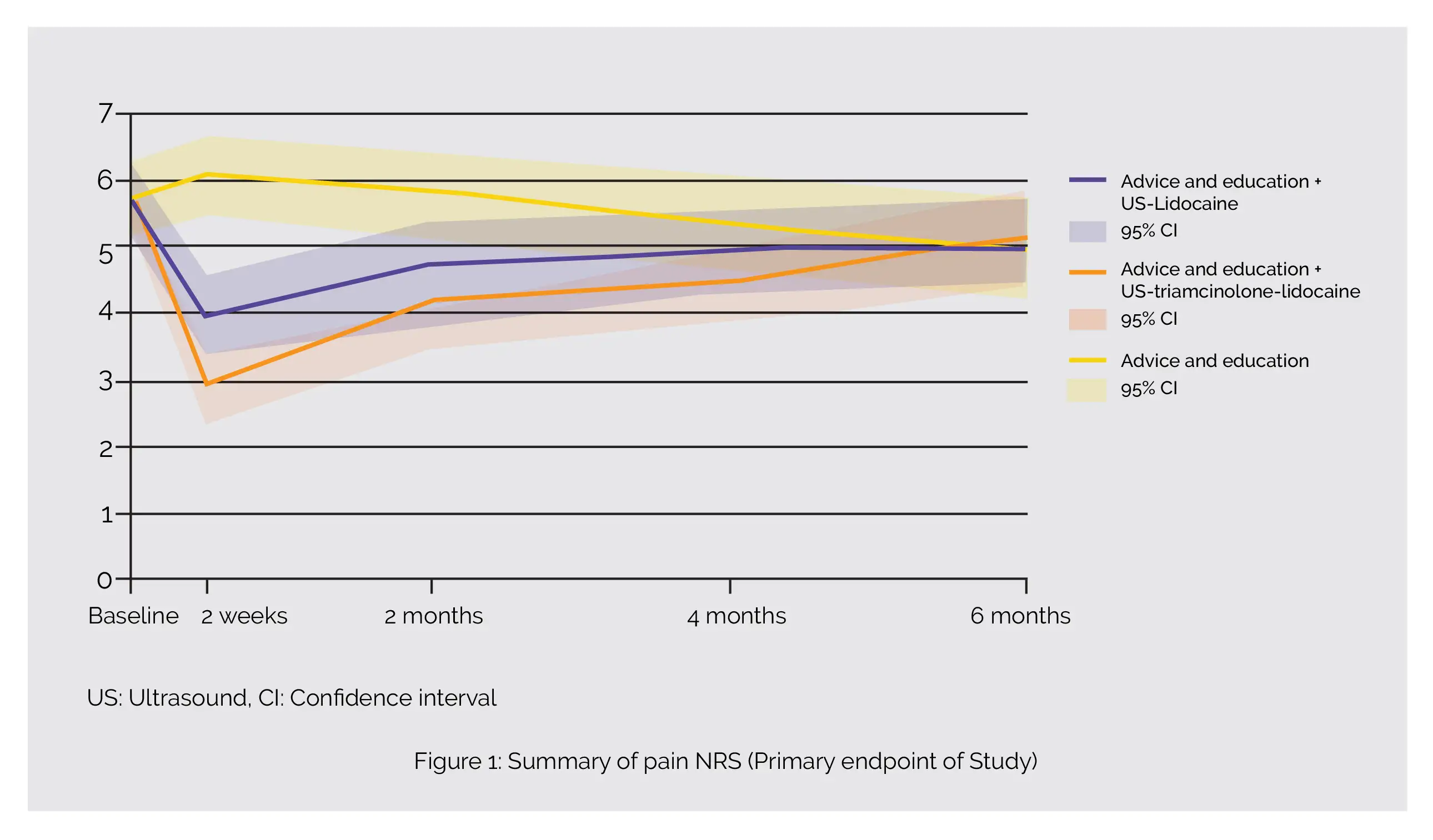
No difference in intensity of hip pain over 6 months was reported between advice and education + ultrasound-triamcinolone-lidocaine compared with advice and education + ultrasound-lidocaine [−0.52 (−1.21 to 0.18)]. The presence of ultrasound confirmed effusion or synovitis was linked to a substantial interaction effect that favored ultrasound-triamcinolone-lidocaine + advice and education [-1.70 (-3.10 to -0.30)].
Notably, 1 patient with a bioprosthetic aortic valve died in the ultrasound-triamcinolone-lidocaine + advice and education group due to subacute bacterial endocarditis 4 months post-treatment. The death was possibly associated with the trial treatment. Hence, the addition of corticosteroid and local anesthetic injection to education and advice is a clinically efficient therapy for sustained and rapid symptom response.
The BMJ
Clinical effectiveness of one ultrasound guided intra-articular corticosteroid and local anaesthetic injection in addition to advice and education for hip osteoarthritis (HIT trial): single blind, parallel group, three arm, randomised controlled trial
Zoe Paskins et al.
Comments (0)