Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Intramuscular injection of autologous serum might be efficient to relieve atopic dermatitis.
According to a preliminary randomized clinical trial published in "Yonsei Medical Journal", the use of autologous serum via intramuscular route may be beneficial in managing atopic dermatitis. Researchers aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of intramuscularly injecting autologous serum in people diagnosed with atopic dermatitis.
A group of 23 adolescent and adult subjects diagnosed with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis participated in the study. The volunteers were randomly divided into 2 groups: One receiving 8 injections of autologous serum intramuscularly (5 mL, n=11), and the other receiving saline injections (5 mL, n=12) over a 4-week period.
The patients were then monitored until week 8. The researchers evaluated alterations in the clinical severity of atopic dermatitis using the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) scale, examined patient-reported Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores, and also recorded side effects that occurred from baseline to week 8.
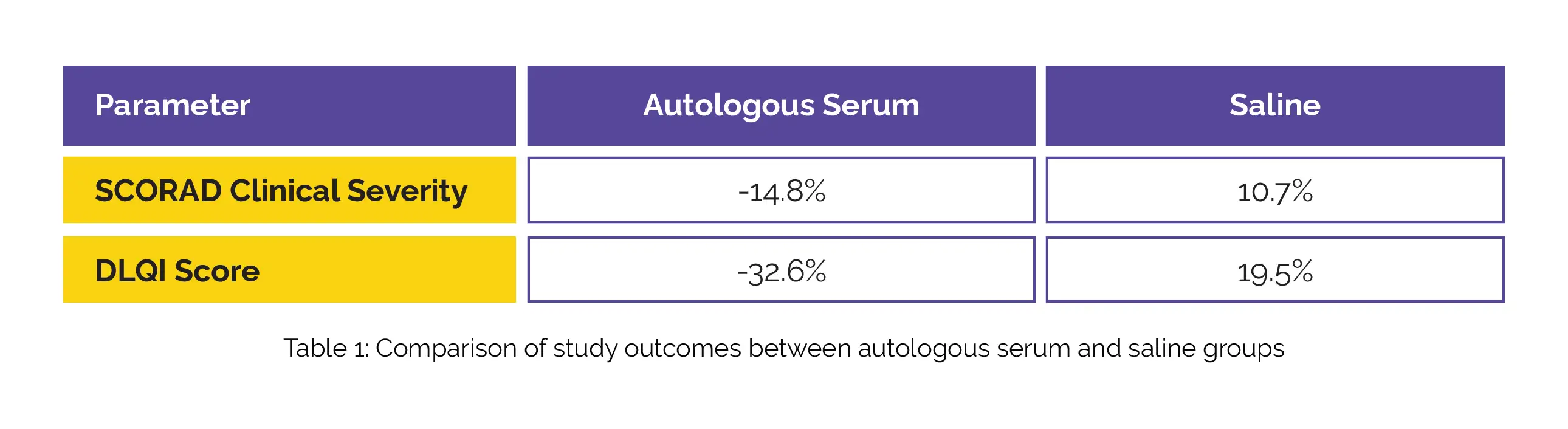
Prior to week 8, one subject from the treatment arm and two subjects from the placebo arm were lost to follow-up. The intramuscular injection of autologous serum led to a better reduction in the SCORAD clinical severity score and an improvement in the DLQI score when compared to the administration of saline. These results are presented in Table 1.
There were no major adverse events reported. The efficacy of intramuscular injection of autologous serum for the management of atopic dermatitis appears promising. However, additional studies are required to thoroughly assess the clinical utility of this intervention for atopic dermatitis.
Yonsei Medical Journal
Intramuscular Injection of Autologous Serum in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Preliminary Randomized Clinical Trial
Dong-Ho Nahm et al.
Comments (0)