Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Oxymetazoline is effective for the management of rosacea, with application-site dermatitis being the most common treatment-emergent adverse event.
The results of a recent meta-analysis indicated that Oxymetazoline is indeed an effective option for the treatment of persistent facial erythema in individuals with rosacea. But, application-site dermatitis is the most significant treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) linked with the use of Oxymetazoline. The objective of the investigators was to assess both the effectiveness and safety of Oxymetazoline as a treatment option for rosacea.
A relevant literature search was performed using databases like PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library. The inclusion criteria encompassed studies that involved randomly assigning patients to either receive Oxymetazoline or a vehicle. Exclusions consisted of systematic reviews, reviews, animal experiments, incomplete research lacking full text or insufficient information for data extraction, and duplicate publications. Data assessment was executed using STATA 15.1.
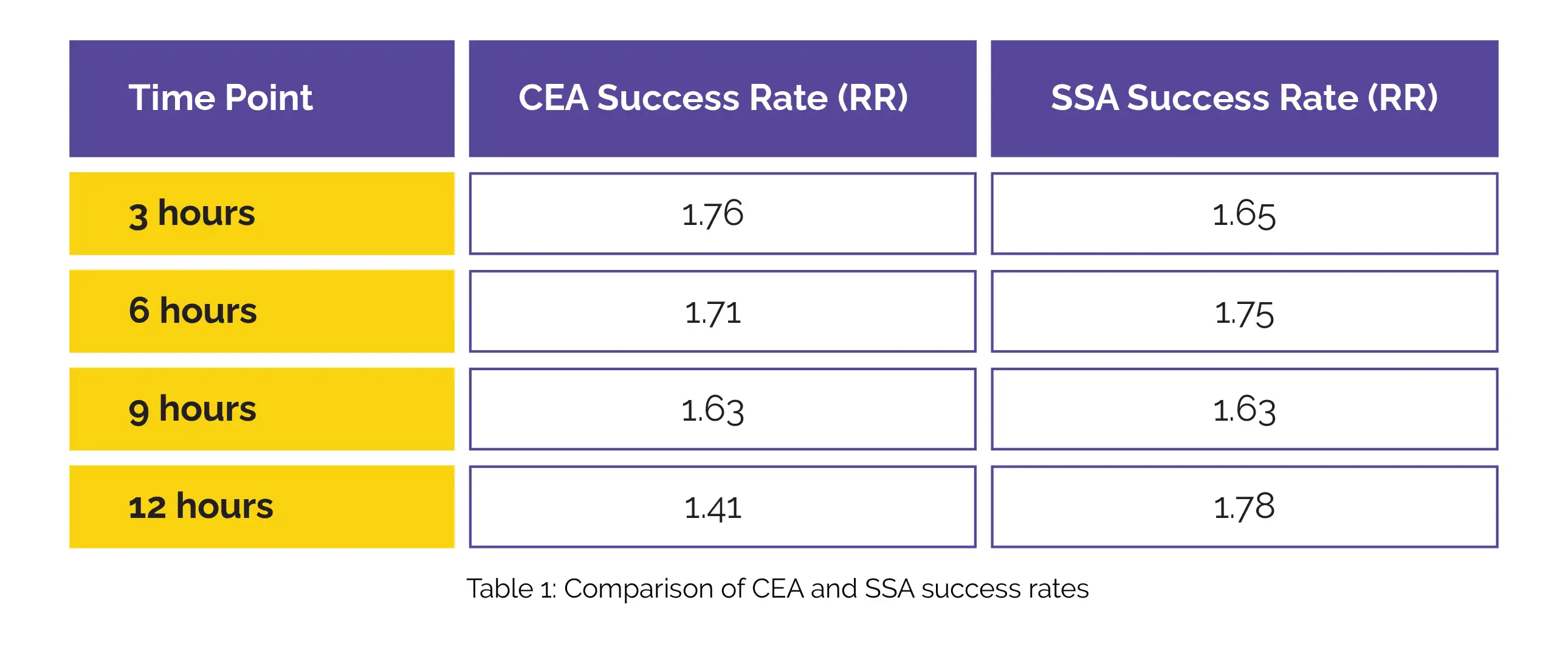
The pooled results demonstrated a statistically significant increase in the success rate of Clinician Erythema Assessment (CEA) (3 hours: ratio rate [RR] = 1.76, 6 hours: RR = 1.71, 9 hours: RR = 1.63, 12 hours: RR = 1.41) and Subject Self-Assessment (SSA) for rosacea facial redness (3 hours: RR = 1.65, 6 hours: RR = 1.75, 9 hours: RR = 1.63, 12 hours: RR = 1.78) after administering Oxymetazoline compared to the vehicle (Table 1).
Furthermore, the analysis revealed a significantly higher incidence of TEAEs with Oxymetazoline compared to the vehicle (RR = 1.34). Notably, the occurrence of application-site dermatitis emerged as the primary TEAE of significance. When examining specific adverse events, the Oxymetazoline group exhibited a significantly higher incidence of application-site dermatitis (RR = 8.91), while no noteworthy difference was witnessed in the occurrence of other adverse events.
Medical practitioners and patients should be cautious about the potential risk of application-site dermatitis associated with Oxymetazoline use. Careful monitoring and appropriate measures can help mitigate this specific adverse event and ensure a positive treatment experience for those with rosacea.
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology
Efficacy and safety of Oxymetazoline for the treatment of rosacea: A meta-analysis
Fei Liu et al.
Comments (0)