Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients with H. pylori infection, Lactobacillus reuteri improves eradication rates, treatment side effects, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
The use of probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri as an adjunct treatment is beneficial for H. pylori-infected patients, according to a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled experiment. Investigators sought to determine if Lactobacillus reuteri was effective in reducing gastrointestinal symptoms triggered by H. pylori as well as the side effects of therapy.
Patients who had just been diagnosed with H. pylori were involved and were given regular triple treatment for 2 weeks, as well as probiotic supplements or a placebo for 4 weeks. In addition to receiving a Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) questionnaire to complete during the trial, patients were also questioned about any treatment-related side effects. 14C urea breath test (UBT) was used to measure the eradication rate following therapy.
A total of 90 eligible participants were enrolled in the trial, with one dropping out (38 men, 51 women, median age: 52.0). Overall, 45 individuals (50.6%) were given a placebo whereas 44 subjects (49.4%) received probiotics. Table 1 depicts the rate of H. pylori eradication in the probiotic group and the placebo group. In the probiotic group, post-treatment GSRS scores for indigestion, constipation, abdominal pain, and overall GSRS revealed a substantial score decrease.
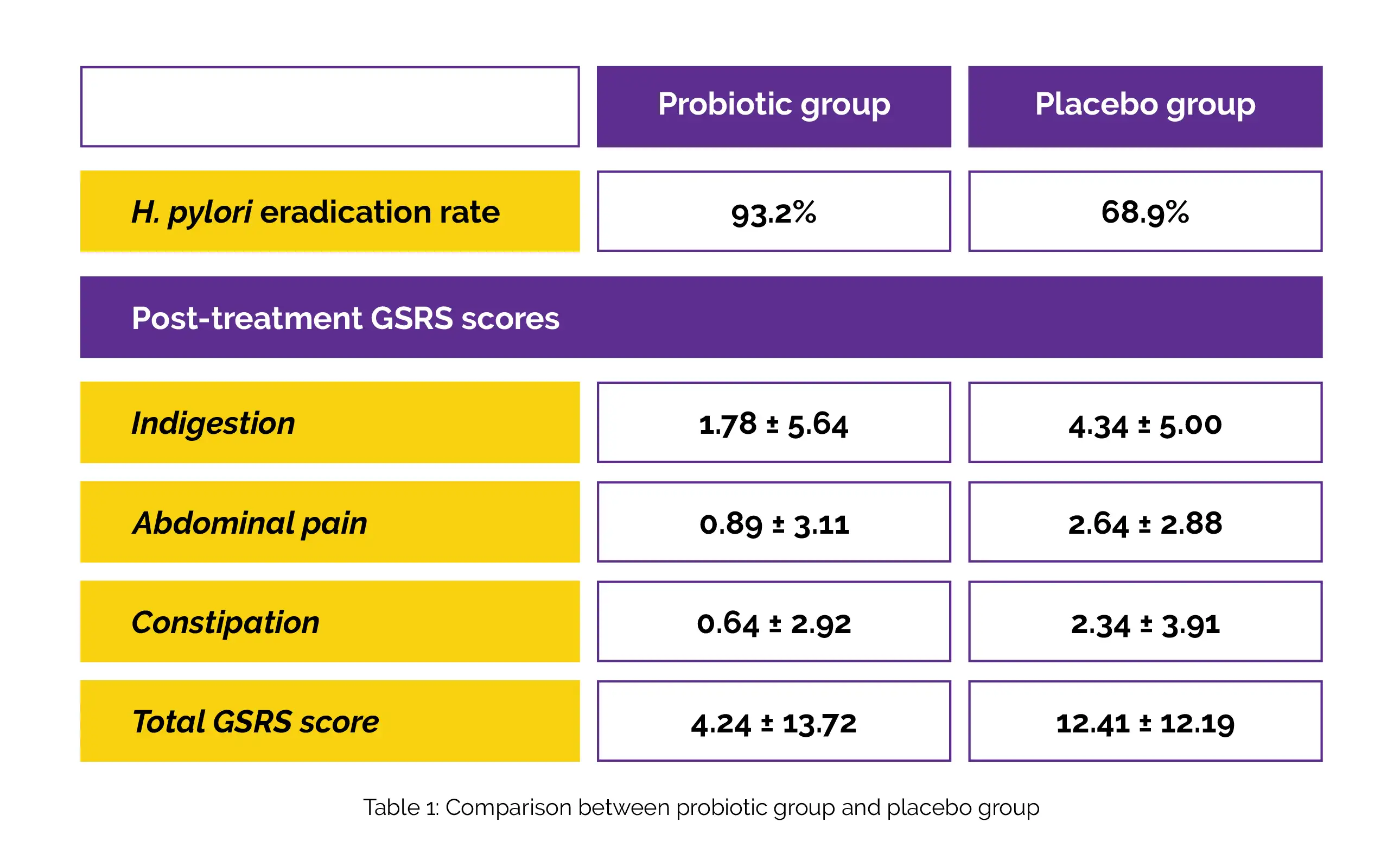
Among the side effects noted, headache and stomach discomfort showed a clinically meaningful difference between the two groups. Hence, the rate of eradication, gastrointestinal symptoms, and side effects of therapy significantly improves when Lactobacillus reuteri is used as an adjuvant treatment for H. pylori infection.
BMJ Journals
IDDF2022-ABS-0107 The effect of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotic as an adjunct treatment for helicobacter pylori infection in adults
Nur Izreena Ismail et al.
Comments (0)