Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In non-hospitalized adults diagnosed with COVID-19, molnupiravir expedites viral RNA clearance and leads to elimination of the infectious virus.
In a phase 2a randomized clinical trial, molnupiravir demonstrated good tolerability, safety, and antiviral efficacy, as shown by decreased infectious virus isolation from nasopharyngeal swabs, less time to elimination of coronavirus RNA, a higher percentage of people who cleared coronavirus RNA, and a significant decline in viral RNA from baseline in comparison with placebo-recipients.
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study, researchers determined the antiviral efficacy, tolerability, and safety of molnupiravir in coronavirus-infected people. Overall, 202 unvaccinated people having confirmed coronavirus infection and with symptom duration of less than seven days were segregated (1:1 ratio) to get 200 mg molnupiravir or placebo. The recruited people were then segregated (3:1 ratio) to get molnupiravir (800 mg or 400 mg) or placebo, orally twice daily for about five days.
Using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), the antiviral effect was evaluated for SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the nasopharyngeal swabs. The major outcome ascertained was the time to viral RNA clearance while detection of infectious virus in swabs was the secondary outcome ascertained.
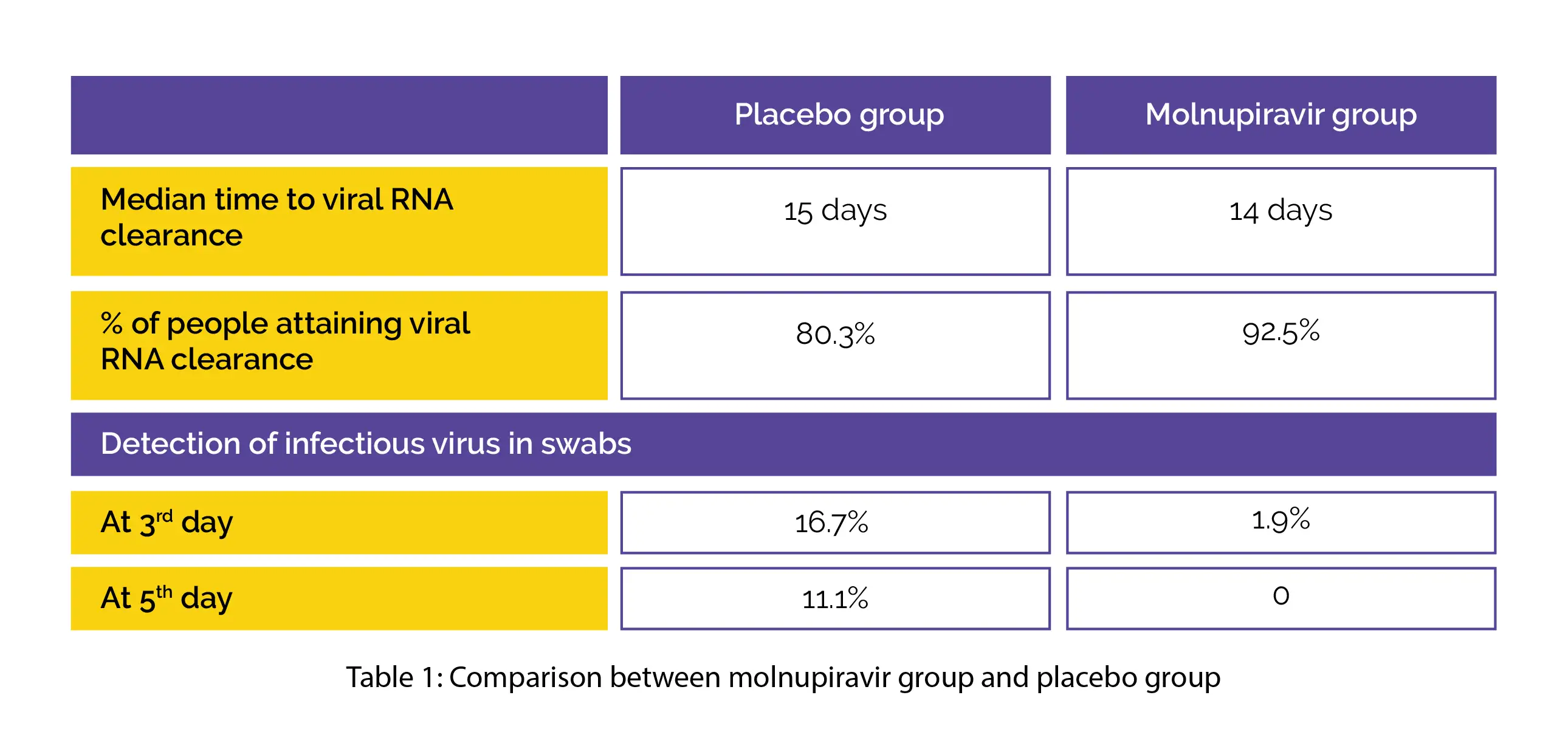
In comparison with the placebo arm, the 800 mg molnupiravir arm exhibited reduced median time to viral RNA clearance (log rank p value=0.013). After four weeks, a greater percentage of 800 mg molnupiravir-recipients attained viral RNA clearance when compared to placebo recipients.
On the third day of therapy, the detection of infectious virus in swabs was less in the 800 mg molnupiravir arm when compared to the placebo arm. On the fifth day of treatment, the infectious virus was not isolated from any volunteer receiving 400 or 800 mg molnupiravir in comparison with the placebo arm, as shown in Table 1:
Molnupiravir showed good tolerability with a comparable number of noxious events across all the dosages. This study offered strong biological evidence favoring the development of molnupiravir as an oral therapeutic agent for reducing replication of the infectious virus and impeding the advancement of COVID-19 during the early stages of the disease.
Science Translational Medicine
A Phase 2a clinical trial of Molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus
William A Fischer et al.
Comments (0)