Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In non-ulcer dyspepsia patients, Saccharomyces boulardii and triple therapy combination can lead to a better elimination effect on H. pylori infection.
A randomized controlled study depicted that the combination of Saccharomyces boulardii (S. boulardii) and triple therapy is safe, effectively relieves symptoms, and expedites eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. G B Yang et al. aimed to evaluate safety and effectiveness of S. boulardii along with triple therapy for H. pylori management in people with non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD).
In this multi-center study, 497 H. pylori-infected people (229 men and 268 women) aged 18-69 years diagnosed with NUD who underwent gastroscopy were recruited and randomly segregated into three groups. Group 1 patients were given S. boulardii for fourteen days and triple therapy for ten days. Bismuth quadruple group was received by group 2 patients for ten days. Group 3 patients were given triple therapy for ten days.
A total of 472 participants (155 cases in group C, 159 cases in group B, and 158 cases in group A) finished the trial. On 44th day of intervention, the status of H. pylori was explored utilizing a 13C-urea breath test. On Day 14 and Day 44, the side effects and improvement in symptoms were evaluated. The intention-to-treat (ITT) and per protocol-based (PP) eradication rates in patients of groups 1, 2 and 3 are depicted in Table 1:
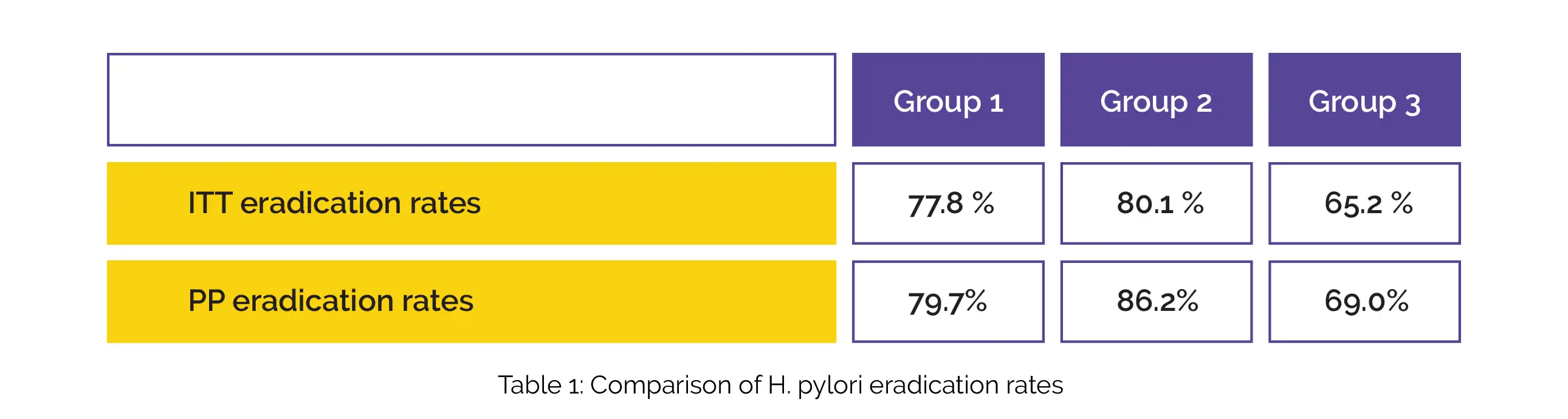
Among three groups, statistically significant differences were observed in ITT and PP analysis. No profound difference between H. pylori elimination rates of two quadruple therapies was seen. However, both of them were substantially greater when compared to standard triple therapy. Compared to standard triple therapy, both quadruple therapies resulted in remarkably greater symptom betterment of belching on day 14.
On day 44, significantly greater alleviation of abdominal distension and belching symptom scores of group 1 were observed compared to group 3. No major side effects were witnessed. A significantly lower occurrence of diarrhea was reported in group 1 compared to groups 2 and 3. The combination of S. Boulardii and triple therapy appears to be a promising first-line regimen for the elimination of H. pylori infection in NUD patients.
Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue za Zhi
[A multi-center, randomized controlled study on the effect of Saccharomyces boulardii combined with triple therapy for the initial eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection]
G B Yang et al.
Comments (0)