Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Rifasutenizol (whether alone or combined) demonstrated safety and tolerance in H. pylori patients, with a 14-day triple therapy showing promise as a new treatment regimen.
Not just as monotherapy, oral Rifasutenizol capsules when combined with Rabeprazole enteric-coated tablets and Amoxicillin capsules (14-day triple therapy) delivered outstanding results for H. pylori-infected individuals in China, as per the results of four clinical trials.
Given the increasing antimicrobial resistance, most H. pylori eradication treatments have become less effective. The clinical development of Rifasutenizol (TNP-2198), a novel antibacterial with dual action, is underway. Xiaojiao Li et al. conducted a study to assess the safety and efficacy of Rifasutenizol for individuals with H. pylori infection.
To solve the basis of this study, 4 clinical trials (shown in Table 1) of Rifasutenizol capsules in healthy people and those who are asymptomatic with H. pylori infection (aged 18 to 65 years) in China were conducted.
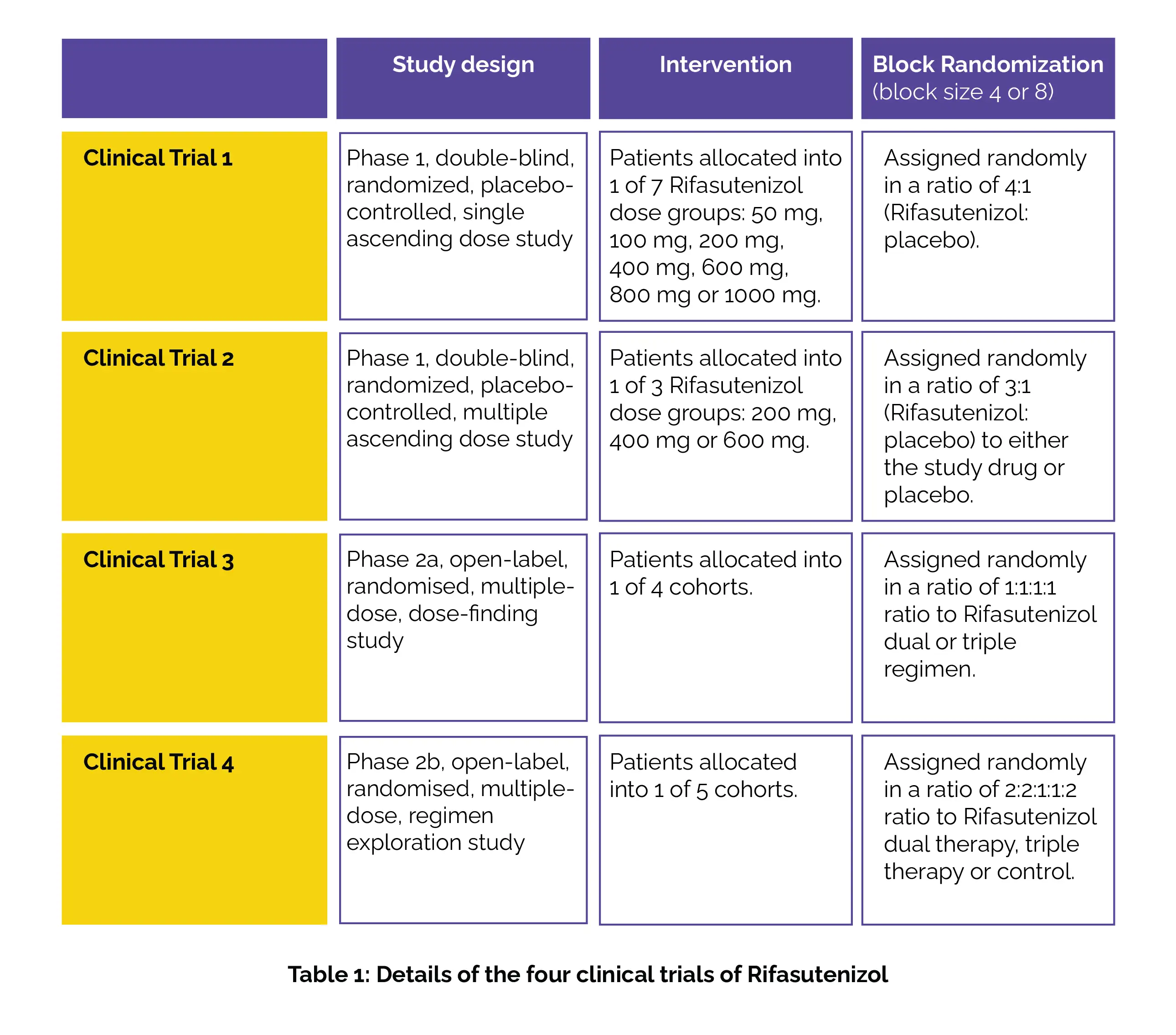
Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetic interactions of Rifasutenizol were the main primary endpoints for clinical trials 1, 2, and 3. Eradication rate of H pylori was the main primary endpoint for clinical trials 4.
As per the study results, 78 healthy people (trial 1: number of patients, n = 10 per cohort; and an additional 8 for the food-effect cohort) and 168 asymptomatic H pylori patients (trial 2: n = 16 per cohort; trial 3: n = 10 per cohort; trial 4: n = 10 or n = 20 per cohort) were allocated between May 9, 2019, and Sept 14, 2022. Single and multiple doses of Rifasutenizol (50–1000 mg and 200–600 mg given two times daily), whether alone or with Rabeprazole and Amoxicillin, exhibited good safety and tolerability.
The majority of adverse events were mild. Also, no evident drug-drug interactions were found between Rifasutenizol and other administered therapies. Consuming food led to a slight increase in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of Rifasutenizol. The geometric mean AUC0–t and AUC0– ∞ in the fed state were 1.334 and 1.396 times higher, respectively, than the fasted state. Mild accumulation was observed with the incessant administration of Rifasutenizol. In trial 3, the Rac (AUC) for Rifasutenizol 400 mg in the dual routine was 1.37 and in the triple routine was 1.49.
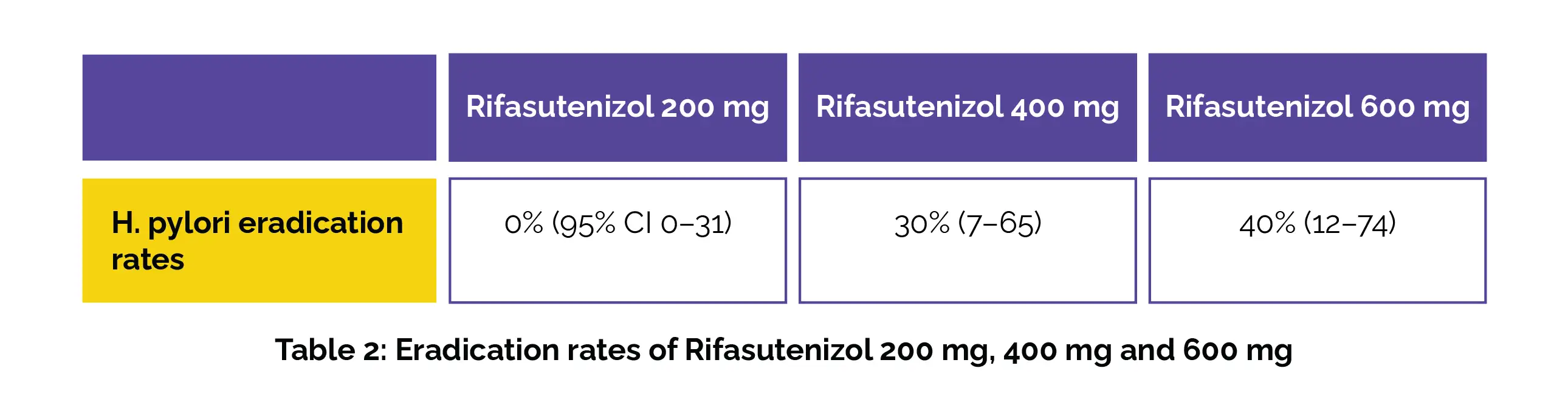
Rifasutenizol dosed at 400 mg was the most effective dose in trial 3. The details of the rates of eradication with different doses given twice a day for 14 days are shown in the following Table 2:
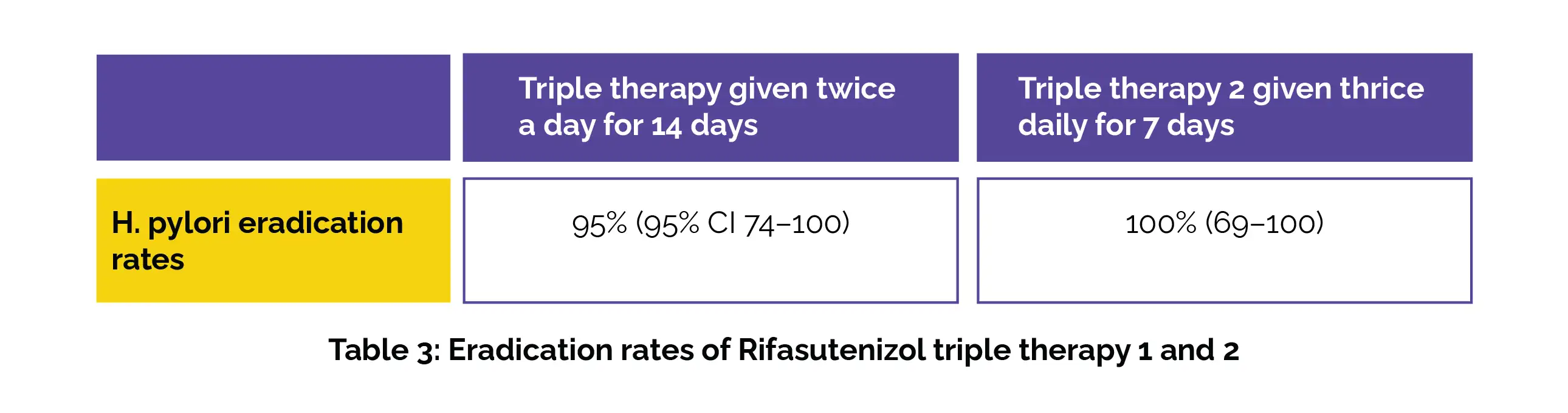
The H pylori eradication rates of Rifasutenizol 400 mg + Rabeprazole sodium 20 mg + Amoxicillin 1 g (triple therapy 1) given twice daily for 14 days and, Rifasutenizol 600 mg + Rabeprazole sodium 20 mg + Amoxicillin 1 g (triple therapy 2) given thrice daily for a week in trial 4 are shown below (Table 3):
Overall, Rifasutenizol has the potential to improve H. pylori infection, as concluded.
The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of Rifasutenizol, a novel dual-targeted antibacterial agent in healthy participants and patients in China with Helicobacter pylori infection: four randomised clinical trials
Xiaojiao Li et al.
Comments (0)