Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The gene expression levels of caspase-3 and CYP2E1 may be utilized as a diagnostic tool for COVID-19 patients.
In a recent study published in "Gene Reports", people affected with coronavirus disease exhibited reduced CYP2E1 and elevated Caspase-3 gene expression levels. The authors sought to examine gene expression CYP2E1 and Caspase-3 and to assess the association between gene expression and demographic-clinical data in people suffering from coronavirus disease.
The study recruited 30 healthy volunteers and 60 COVID-19(+) people (non-ICU and ICU patients). With the help of quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), the level of gene expression was estimated. For analyzing gene expression, the 2-ΔΔCt methodology was used.
The expression of Caspase-3 and CYP2E1 genes depicted a profound discrepancy between SARS-CoV-2 people and healthy volunteers. In comparison with healthy individuals, the coronavirus-infected people exhibited an elevated expression of caspase-3 and reduced expression of CYP2E1, as shown in Figure 1:
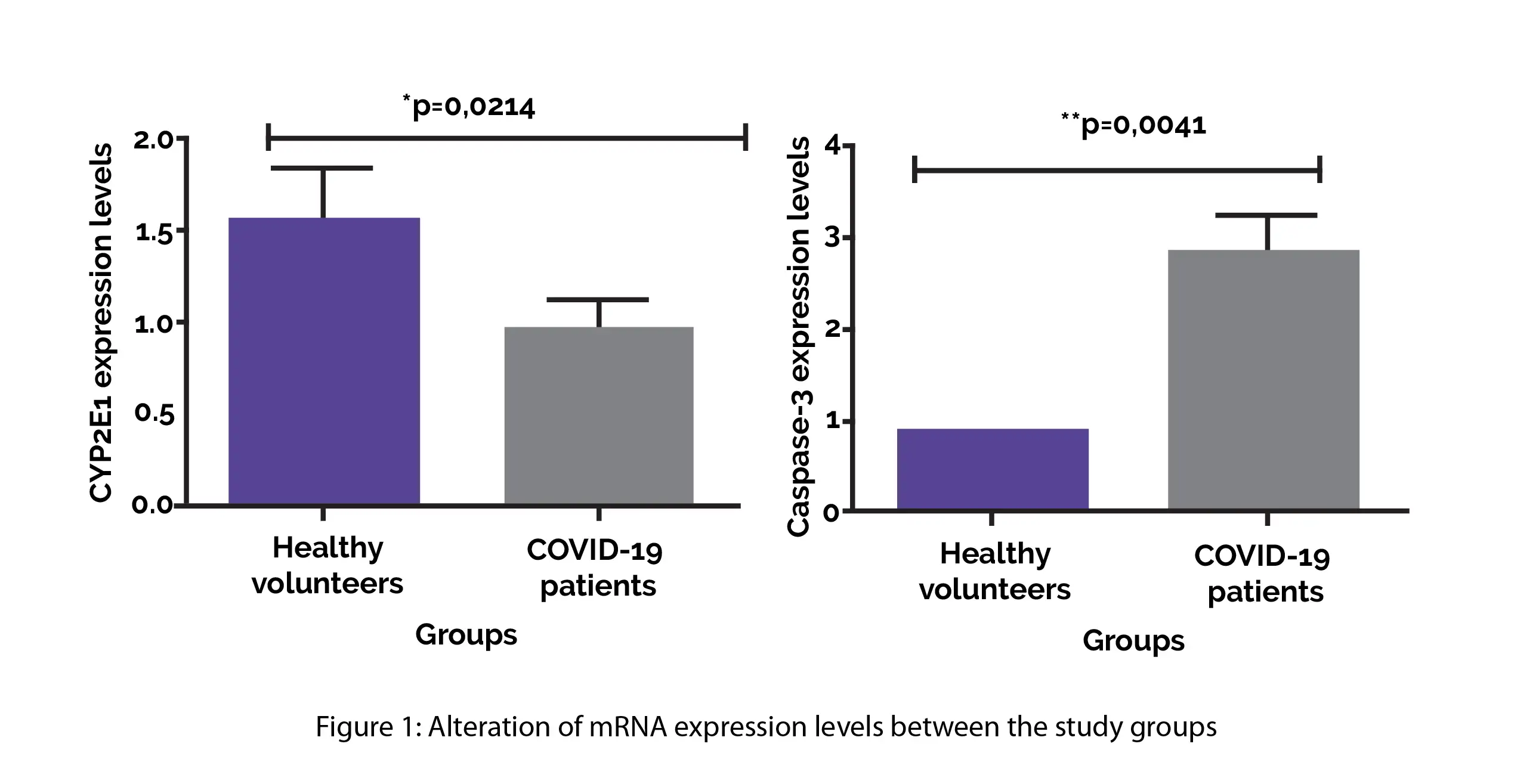
Compared to people having unaffected lungs, people having affected lungs exhibited reduced expression levels of both genes. The lab findings including lymphocyte count, d-Dimer, platelet count, lactate dehydrogenase were associated with both the gene expressions. No correlation was noted between Caspase-3 and CYP2E1 expressions.
The Caspase-3 expression indicated apoptotic situations of patients. However, it was not linked with the expression level of CYP2E1. For metabolizing xenobiotics and endogens, CYP2E1 gene expression is a pivotal factor. But, SARS-CoV-2 people showed reduced expression of CYP2E1.
Gene Reports
Investigation of CYP2E1 and Caspase-3 Gene Expressions in COVID-19 patients
S.Karabulut Uzuncakmak et al.
Comments (0)