Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


50 mg Tegoprazan is superior to 40 mg Esomeprazole for rectifying nocturnal symptoms and sleep disturbances in GERD patients.
In gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)-affected people, Tegoprazan may improve sleep disorders related to nocturnal heartburn and may result in a quicker remission of nighttime heartburn symptoms, as deciphered from a multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled study.
The purpose of the study was to compare the effectiveness of Tegoprazan with Esomeprazole in treating GERD patients' nighttime heartburn and sleep problems. Patients were randomized to receive either 50 mg Tegoprazan or 40 mg Esomeprazole for two weeks if they had sleep difficulties, nocturnal heartburn, or erosive esophagitis. The time to the first interval without nighttime heartburn served as the major outcome. A comparison of the percentage of nighttime heartburn-free days was also done.
Overall, 46 subjects were recruited. Tegoprazan shortened the time to the first nighttime heartburn-free interval compared to Esomeprazole, although the difference was not clinically meaningful. The Tegoprazan group had a larger proportion of nights without experiencing heartburn, although the difference between the two groups was negligible, as shown in Table 1:
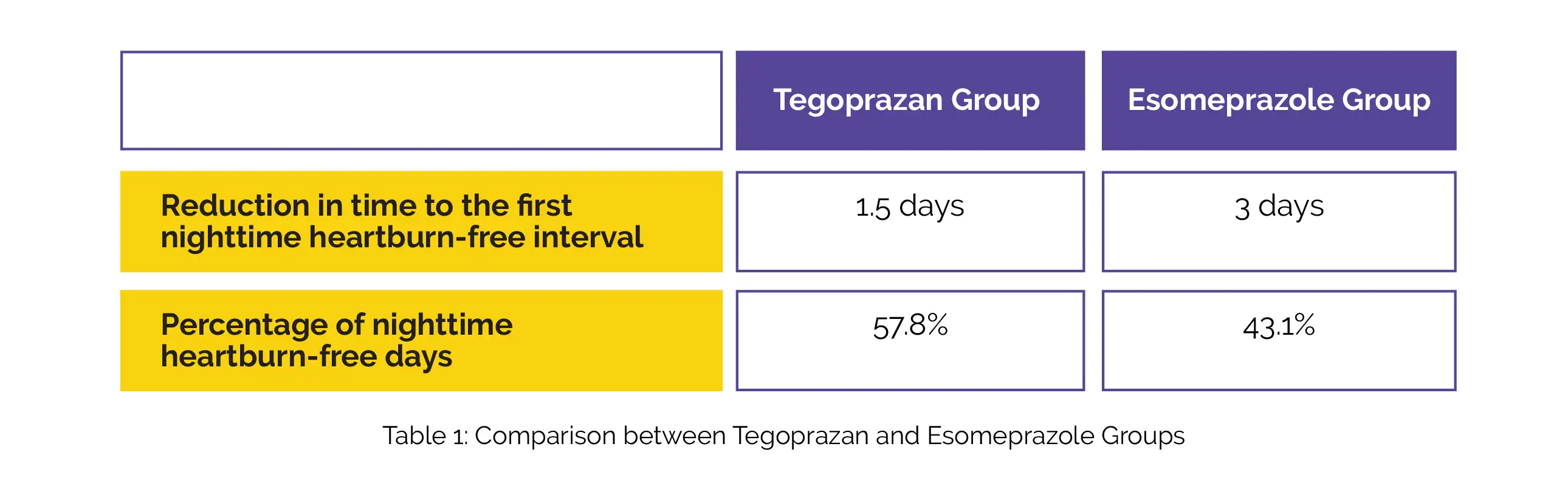
Two patients experienced adverse events. The severity was mild. Therefore, 50 mg Tegoprazan may be more effective than 40 mg Esomeprazole for rapid and sustained alleviation of nocturnal heartburn symptoms. This may lead to improvement in sleep quality and life quality in individuals who experience nighttime heartburn.
Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
Effects of Tegoprazan Versus Esomeprazole on Nighttime Heartburn and Sleep Quality in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Multicenter Double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Joon Sung Kim et al.
Comments (0)