Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder mainly affecting women. This debilitating ailment is characterized by widespread pain, tenderness, and fatigue.
Milnacipran and pregabalin are among the pharmacological agents newly available for treating fibromyalgia, alongside non-pharmacological approaches like mindfulness-based stress reduction and aquatic exercise. These developments expand the range of options for improving fibromyalgia care and alleviating symptoms.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder mainly affecting women. This debilitating ailment is characterized by widespread pain, tenderness, and fatigue. Even with comprehensive research, its cause remains unclear, and there is no known cure. Its deep impact on daily living highlights the pressing need for effective therapies. Recent advancements offer novel avenues for addressing fibromyalgia.
While pharmacological treatments like antidepressants and muscle relaxants can yield relief, their side effects have led to the development of non-pharmacological approaches. Techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exercise, acupuncture, and massage therapy have demonstrated promise in mitigating pain and fatigue. Additionally, lifestyle changes like better sleep hygiene and stress management are also fundamental for symptom management.
For fibromyalgia cure, recent advances encompass new pharmacological agents like milnacipran and pregabalin, as well as non-pharmacological approaches like aquatic exercise and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). These methods have illustrated promising results in attenuating clinical signs and promoting a better quality of life. Healthcare professionals must stay updated on these developments to offer comprehensive, evidence-based care and effectively tackle the complex symptoms of fibromyalgia.
RATIONALE BEHIND RESEARCH
Fibromyalgia is a multifaceted chronic pain syndrome that greatly affects the quality of life. Its elusive etiology highlights the necessity for efficient therapeutic strategies. Hence, this study was conducted.
OBJECTIVE
The aim was to summarize current therapeutic options for fibromyalgia, highlight recent updates, and evaluate the evidence supporting these advancements. It also aimed to enhance medical care professionals' knowledge and support informed decision-making to yield optimal care.
Literature search
Relevant papers issued between 2000 and 2023 were found by searching databases, including Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and MEDLINE. The following search terms were integrated with Boolean operators: advancements, alternative, complementary, developments, fibromyalgia, innovative, intervention, latest, novel, non-pharmacological, pharmacological, therapy, treatment.
Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
Study selection and data extraction
With the assistance of a structured data extraction tool, two reviewers separately retrieved data from the eligible manuscripts. Information on participant characteristics, intervention type, research design, outcome measures, and findings were all incorporated in the data extraction form.
Data and statistical analysis
N/A
Risk of bias and quality assessment
Two separate reviewers scrutinized the integrity of the included research employing suitable tools (for instance, the Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tool and the Cochrane risk of bias tool). In case of discrepancies, a third opinion was requested. The study was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) and adhered to referred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.
The review process was rendered reproducible, transparent, and of high quality. This approach significantly bolstered the review's credibility and validity.
Study outcomes
(a) Primary or secondary outcome measures linked to FMS cure, such as quality of life, physical function, pain, or other FMS-linked symptoms.
(b) Adverse events related to the interventions used.
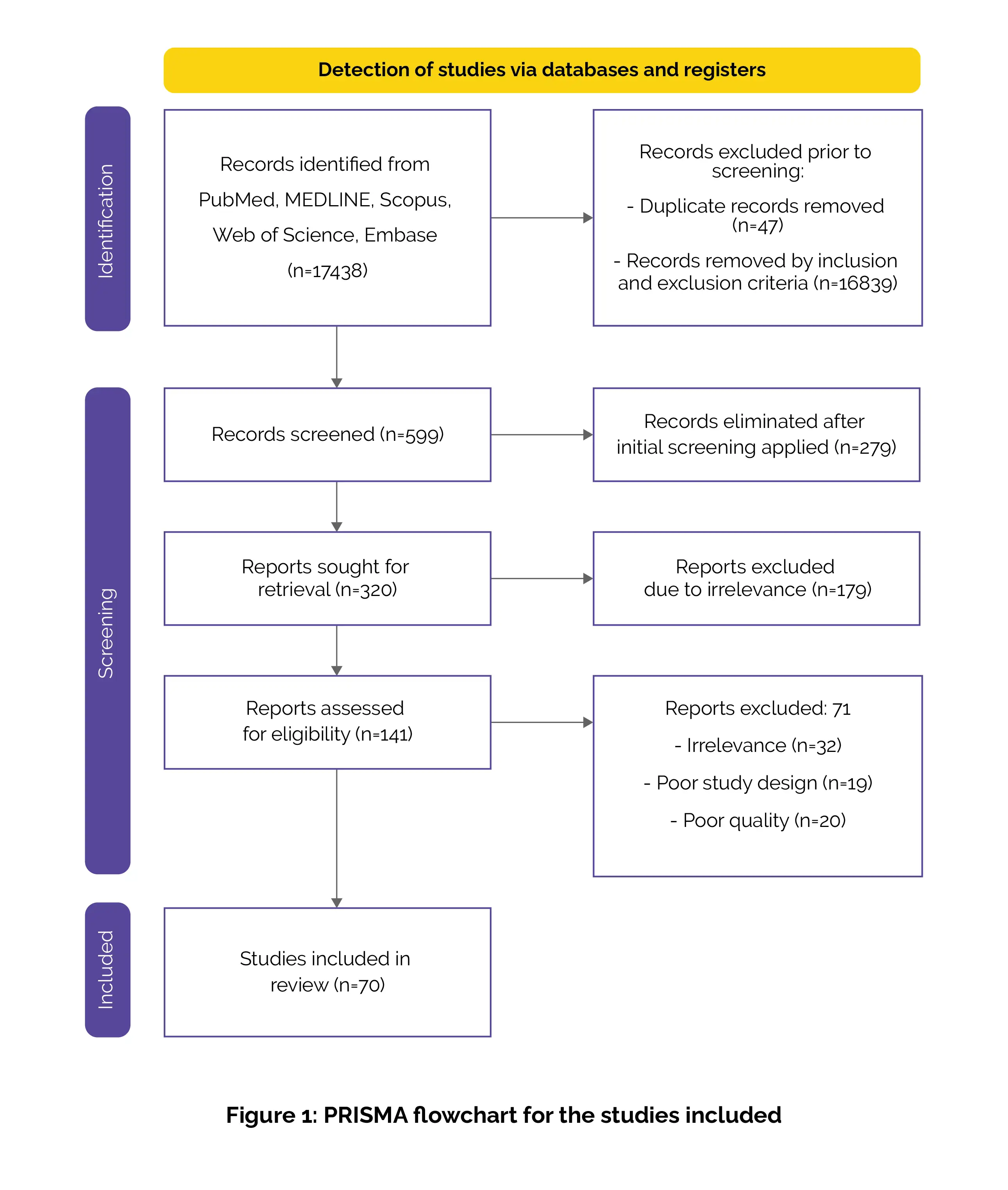
Outcomes
Study and participant characteristics:
N/A
Study quality:
N/A
Effect of intervention on the outcome:
[1] Current Treatment Strategies for Fibromyalgia: An Overview
[2] Advances in Fibromyalgia Treatment: Latest Insights
[a] Pharmacological treatments
1. SNRIs
(a) Milnacipran
(b) Duloxetine
2. Anticonvulsants
(a) Pregabalin
(b) Mirogabalin
(c) Lacosamide
3. Cannabinoids
4. Tropisetron
5. Sodium oxybate
[b] Non-pharmacological treatments
1. Mind-body interventions
2. Exercise therapy
3. Acupuncture
4. TENS
5. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
6. Hydrotherapy
7. Yoga therapy
8. Music therapy
9. Mindfulness-based art therapy
10. Tai chi
11. Virtual reality distraction therapy
12. CBT
13. MBSR
14. Graded exercise therapy
15. Occupational therapy
16. Massage therapy
17. Dietary supplements
Fibromyalgia affects millions globally with a complex mix of genetic, environmental, and psychological causes. Diagnosis of this chronic pain ailment is guided by symptoms and the elimination of other conditions. Though it impacts quality of life, a multidisciplinary approach helps manage the condition effectively, allowing patients to lead fulfilling lives. Staying current on treatment strategies is key to optimal care.
This review used clear inclusion criteria and an extensive search strategy to ascertain relevance and thoroughness. It offered valuable clinical insights on the effectiveness and safety of fibromyalgia therapies, with transparency enhanced by detailed methods and adherence to PRISMA guidelines. Studies were critically appraised utilizing the Cochrane tool and GRADE approach, improving reliability, while the inclusion of diverse populations increased generalizability. Registration with PROSPERO further strengthened the review's rigor. For fibromyalgia management, medications like duloxetine, pregabalin, and milnacipran should be considered for pain alleviation.
Include exercise therapy, like aerobic and resistance training, in the intervention plan. CBT can aid to reduce pain, boost life quality, and relieve mood disorders. Mind-body holistic therapies like tai chi and yoga practices can also relieve pain and boost physical function. Educate patients about fibromyalgia for better outcomes and use a multi-modal, personalized therapeutic approach. Involving patients in decision-making and ensuring early intervention with regular symptom monitoring is fundamental for optimal results. Future research could explore:
Treatment of fibromyalgia, a chronic pain disorder, requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating both pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies. Latest developments yield novel interventions to lessen symptoms and boost overall well-being. Healthcare personnel must stay updated on these advancements to deliver effective, evidence-based care and improve patient outcomes.
Cureus
Beyond the Pain: A Systematic Narrative Review of the Latest Advancements in Fibromyalgia Treatment
Pothuri R Ram et al.
Comments (0)