Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with the goal of investigating the performance of machine learning algorithms in forecasting viral hepatitis.
The support vector machine algorithm shows the best performance in predicting hepatitis B, while the k-nearest neighbour algorithm excels in predicting hepatitis C.
A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with the goal of investigating the performance of machine learning algorithms in forecasting viral hepatitis.
English-language publications that focused on anticipating hepatitis through machine learning algorithms were incorporated by conducting a thorough literature search across databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus. Two authors independently extracted pertinent data from chosen studies.
The study selection and reporting of results were guided by adherence to the PRISMA 2020 checklist, and the evaluation of the risk of bias was carried out utilizing the International Journal of Medical Informatics (IJMEDI) checklist. Utilizing the 'metandi' command in Stata 17, data analysis was carried out.
A total of 21 distinct studies were incorporated, encompassing 82 algorithms. Among these, 16 studies employed 5 algorithms for predicting hepatitis B, while 10 studies utilized the same number of algorithms for predicting hepatitis C.
In the context of hepatitis B prediction, support vector machine (SVM) algorithms displayed the greatest sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR). Conversely, for hepatitis C prediction, k-nearest neighbour (KNN) algorithms demonstrated the highest sensitivity, specificity, and DOR (Table 1).
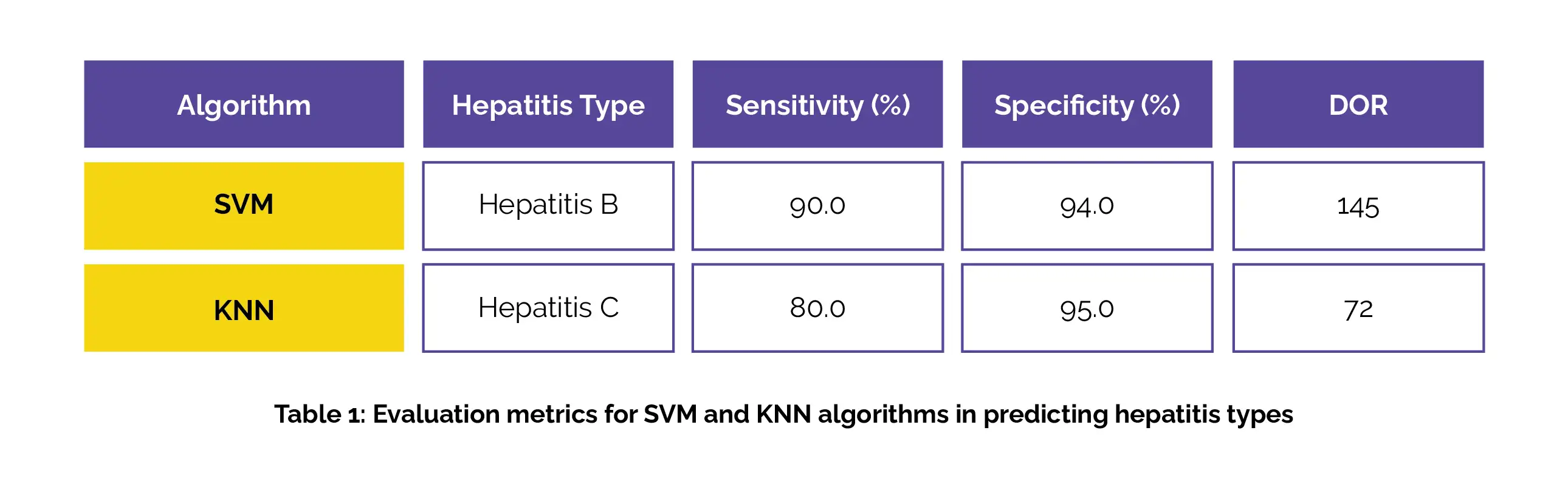
To sum up, the machine learning algorithms SVM and KNN demonstrated impressive performance in predicting hepatitis. SVM excelled in forecasting hepatitis B, while KNN proved to be more efficient in predicting hepatitis C. This suggested a considerable potential for these algorithms to enhance timely and accurate diagnosis in clinical practice, thereby improving hepatitis prediction and management.
International Journal of Medical Informatics
Machine learning for prediction of viral hepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Khadijeh Moulaei et al.
Comments (0)