Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The objective of this study was to compare the analgesic effectiveness between low-dose Ketorolac and Parecoxib subsequent to total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Compared to Parecoxib, preemptive administration of low-dose Ketorolac appears to be effective for pain control in the initial 24 hours following total knee arthroplasty, suggesting a possible reduction in opioid usage.
The objective of this study was to compare the analgesic effectiveness between low-dose Ketorolac and Parecoxib subsequent to total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
This retrospective cohort study was executed with 200 subjects who underwent knee surgery. The participants were divided into two groups:
Pain scores, opioid consumption, and adverse events were assessed.
Superior results compared to Parecoxib were revealed by Ketorolac in this investigation. Patients administered Ketorolac reported notably reduced Visual Numeric Rating Scale (VNRS) scores at 8- and 20-hours post-surgery, as shown in Figure 1:
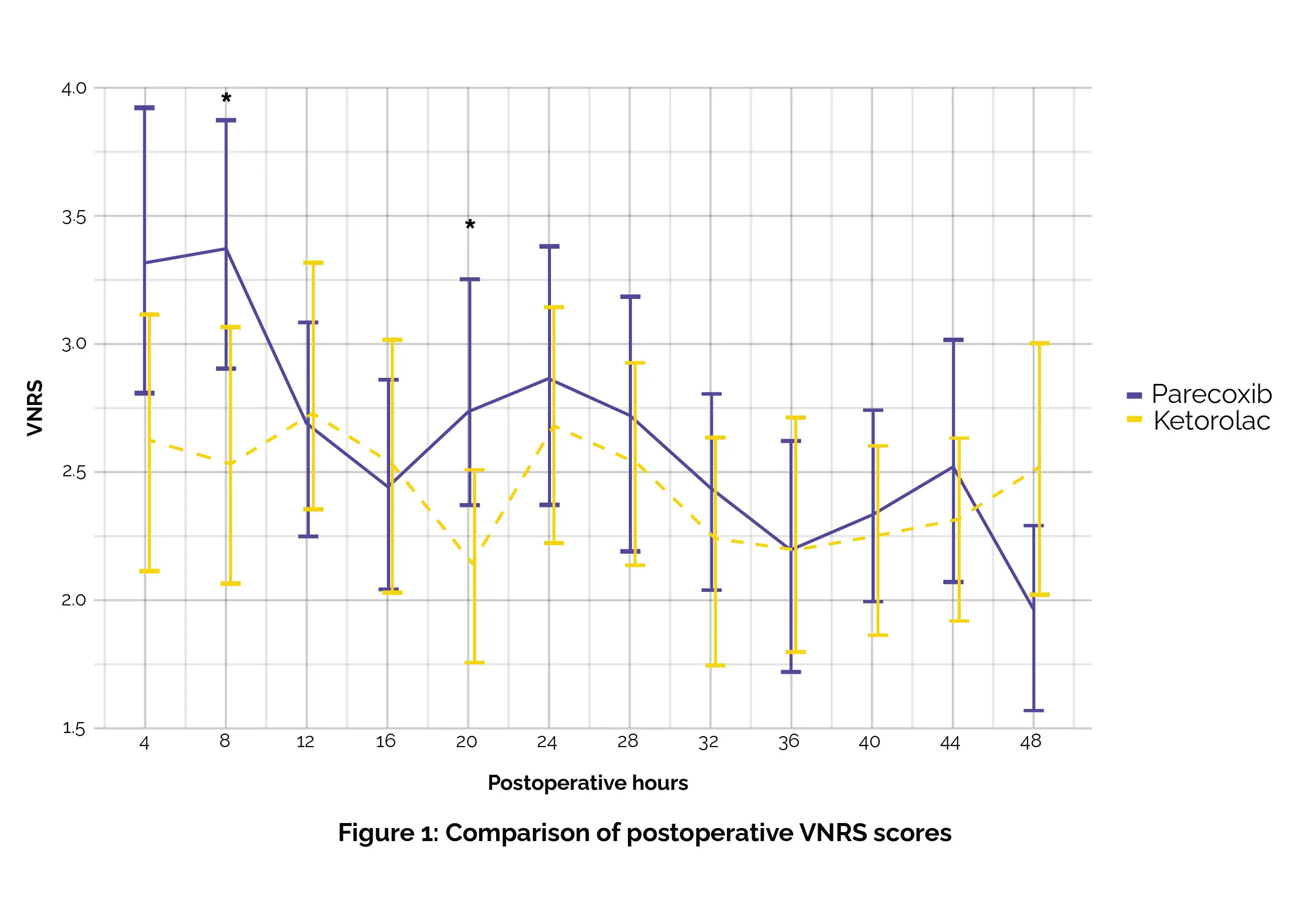
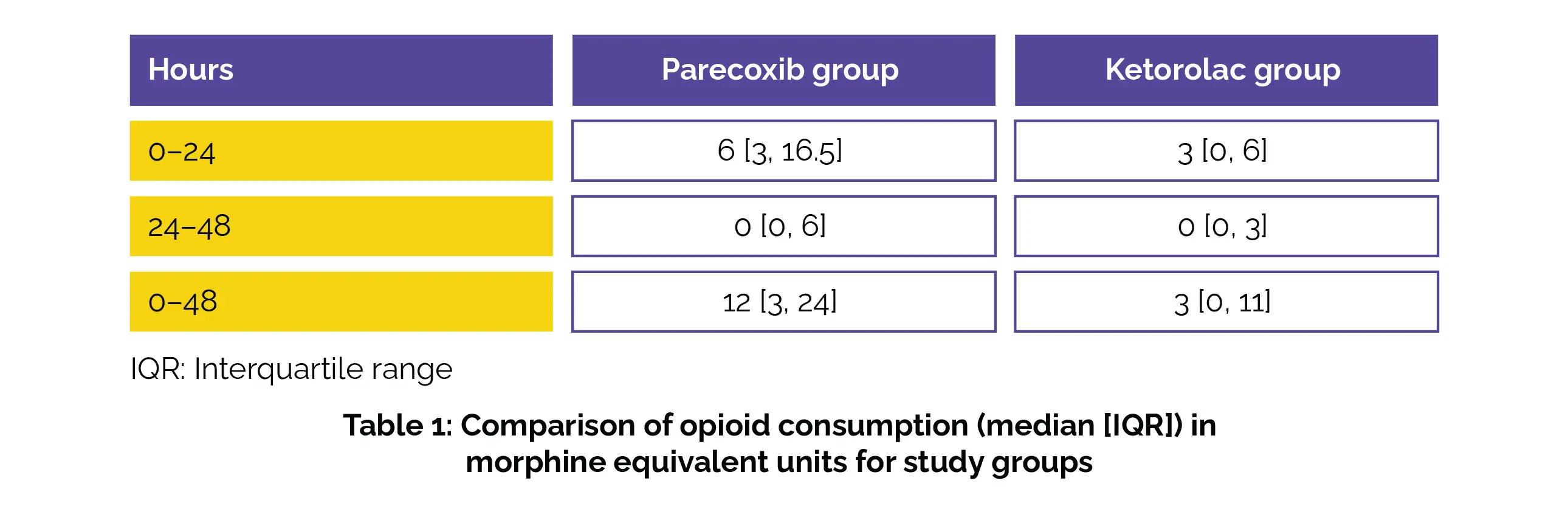
This pattern was additionally validated through linear mixed models (p = .0084). Furthermore, reduced opioid use during the initial 24 hours was associated with Ketorolac (Table 1).
Importantly, the incidence of adverse events showed no significant difference between the two groups.
Superior analgesic efficacy during the initial 24 hours after TKA was demonstrated by preemptive analgesia with low-dose Ketorolac compared to Parecoxib. These findings contribute to the increasing body of evidence indicating a potential analgesic ceiling effect with Ketorolac.
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery
Superior analgesic efficacy of preemptive low-dose ketorolac compared with parecoxib after total knee arthroplasty: A retrospective propensity score matching study
Khanin Iamthanaporn et al.
Comments (1)