Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Patients with COVID-19 are at a higher risk for arterial and venous thrombosis which can worsen therapy outcomes. This analysis assessed the risks of bleeding and thrombosis in those treated with low molecular weight heparin or Fondaparinux (LMWH/F) and measured the mortality or death rates.
Integration of low molecular weight heparin into standard care protocols could significantly enhance patient management, reducing the risk of VTE complications while maintaining a focus on overall patient safety in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Patients with COVID-19 are at a higher risk for arterial and venous thrombosis which can worsen therapy outcomes. This analysis assessed the risks of bleeding and thrombosis in those treated with low molecular weight heparin or Fondaparinux (LMWH/F) and measured the mortality or death rates.
This systematic review and meta-analysis was based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). To find observational cohort studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the use of LMWH/F in confirmed COVID-19 patients, a search was performed across renowned databases (PubMed, Scopus, Clinicaltrials.gov and Web of Science).
Overall, 220 participants from two studies were analyzed. Compared to patients who received LMWH, the patients who were treated with Fondaparinux were less prone to developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), pulmonary or lung embolism, and deep vein thrombosis (Table 1):
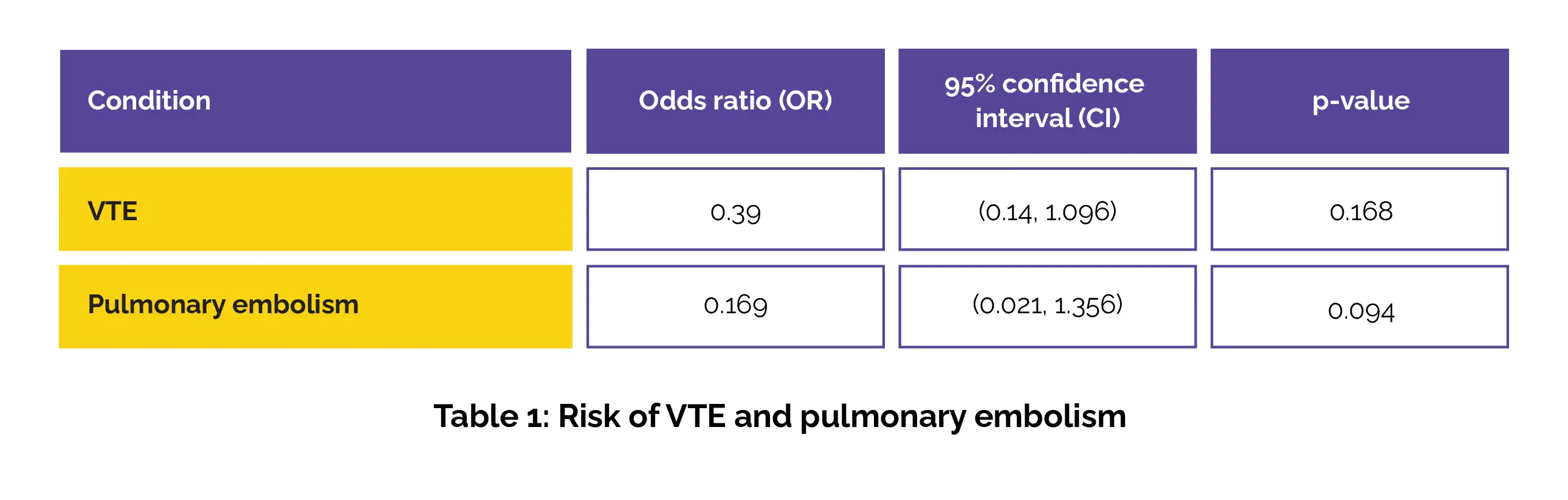
LMWH group had a lower mortality rate (OR 1.135) and fewer instances of bleeding (OR 1.657). Both therapies demonstrated anti-thrombotic effects in COVID-19 patients, with Fondaparinux appearing somewhat more effective in reducing thrombosis occurrences.
LMWH can be safely used for VTE prevention in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, as indicated by bleeding and mortality outcomes.
Cureus
Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Low Molecular Weight Heparins and Fondaparinux in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Shareef L G et al.
Comments (0)