Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A pilot sham-controlled trial aimed to compare the efficacy of the gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) with a sham procedure to improve symptoms and gastric emptying in severe and refractory gastroparesis patients.
In patients diagnosed with gastroparesis, endoscopic pyloromyotomy was found to be better than sham procedure to improve symptoms and gastric emptying six months following the procedure.
A pilot sham-controlled trial aimed to compare the efficacy of the gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) with a sham procedure to improve symptoms and gastric emptying in severe and refractory gastroparesis patients.
Overall, 41 people (11 idiopathic, 13 postsurgical, and 17 diabetic gastroparesis) were randomly divided into G-POEM (n = 21) and sham group (n=20). In this prospective randomized trial, the percentage of patients with treatment success at six months (reduction in Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index [GCSI] by at least 50%) was the major outcome ascertained. People with persistent symptoms were randomized to the sham group and were offered cross-over endoscopic pyloromyotomy.
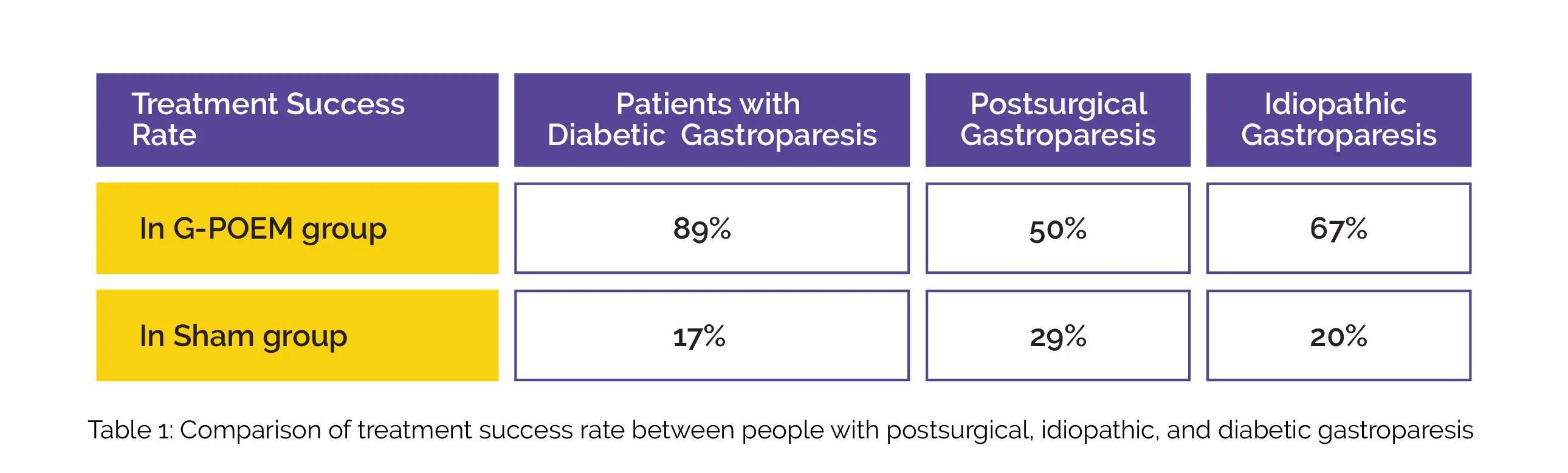
Notably, the treatment success rate came out to be 71% following endoscopic pyloromyotomy and 22% after sham procedure. Following G-POEM and sham procedure, the treatment success in people with idiopathic, postsurgical, and diabetic gastroparesis is depicted in Table 1.
After G-POEM, a reduction in median gastric retention at 4 hours was observed from 22% to 12%. No alteration in median gastric retention was observed after sham (26% versus 24%). Notably, 12 patients crossed over to G-POEM with nine of them (75%) attaining treatment success.
G-POEM was found to be beneficial to improve symptoms and gastric emptying in a substantial percentage of people with severe and refractory gastroparesis.
Endoscopy
Endoscopic pyloromyotomy for the treatment of severe and refractory gastroparesis: a pilot, randomised, sham-controlled trial
Jan Martinek et al.
Comments (0)