Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The purpose of a single-center prospective study was to assess the efficacy of three eradication regimens against H. pylori infection in children.
As a first-line therapeutic option in pediatrics, triple therapy with Metronidazole + Proton pump inhibitor + Amoxicillin for 14 days can attain a higher H. pylori elimination rate.
The purpose of a single-center prospective study was to assess the efficacy of three eradication regimens against H. pylori infection in children.
H. pylori-infected children aged 6 to 17 years were recruited. Volunteers were randomly allocated to receive either sequential treatment, Clarithromycin therapy (CLR), or Metronidazole (MTZ) therapy. By analyzing faecal antigen, the efficacy of the eradication therapy was assessed 4–8 weeks following therapy cessation.
A total of 149 patients were included over an 18-month period. The eradication rate and side effects reported in proton pump inhibitor (PPI) + Amoxicillin (AMO) + MTZ, PPI + AMO + CLR, and sequential therapy, are shown in Figure 1:
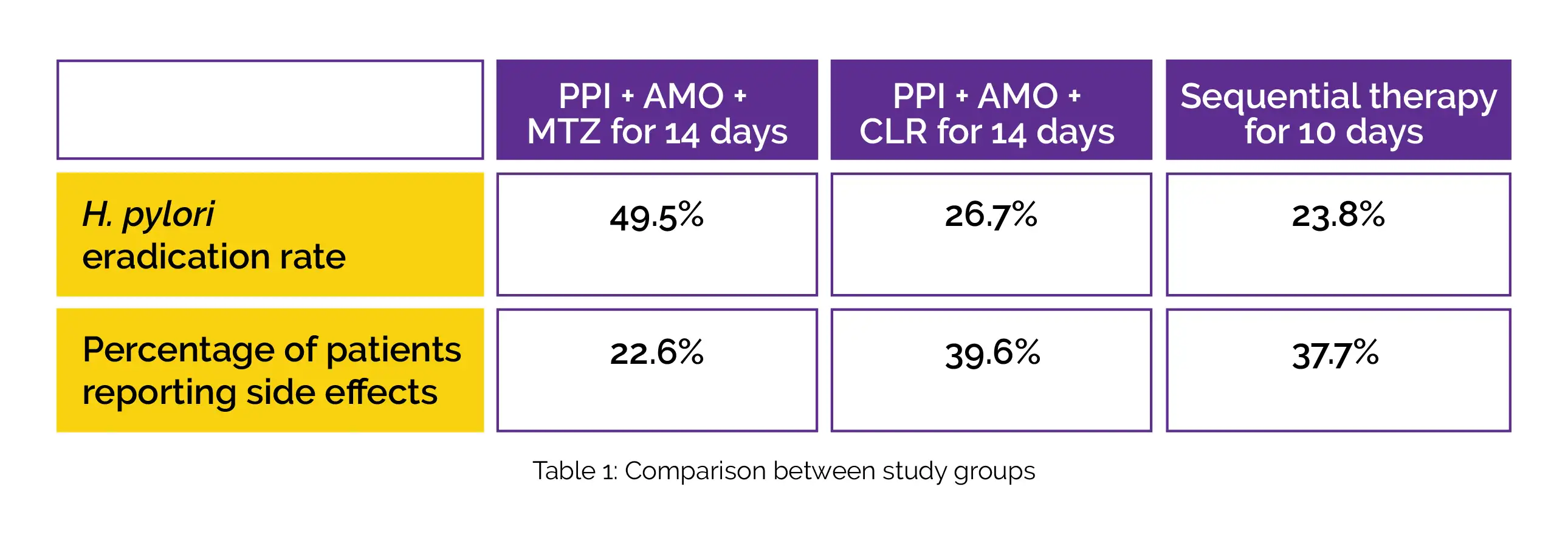
MTZ therapy but not sequential therapy was superior to CLR therapy.
As a first-line therapy, MTZ-based therapy has the potential to effectively eradicate H. pylori.
Children
The Effectiveness of Different Eradication Schemes for Pediatric Helicobacter pylori Infection—A Single-Center Comparative Study from Romania
Oana-Maria Rosu et al.
Comments (0)