Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Gout, an inflammatory condition, has been observed to contribute to the onset and progression of cardiovascular events such as coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Gout is linked to an increased risk of major cardiovascular events, especially in men.
Gout, an inflammatory condition, has been observed to contribute to the onset and progression of cardiovascular events such as coronary artery disease and heart failure. This study sought to examine the link between gout and subsequent cardiovascular events.
This retrospective cohort study analyzed 66,000 gout patients versus 66,000 matched non-gout individuals from 2005 to 2020. Incidence of angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and chronic coronary heart disease were compared.
Table 1 below summarizes the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in gout and non-gout patients over 10 years:
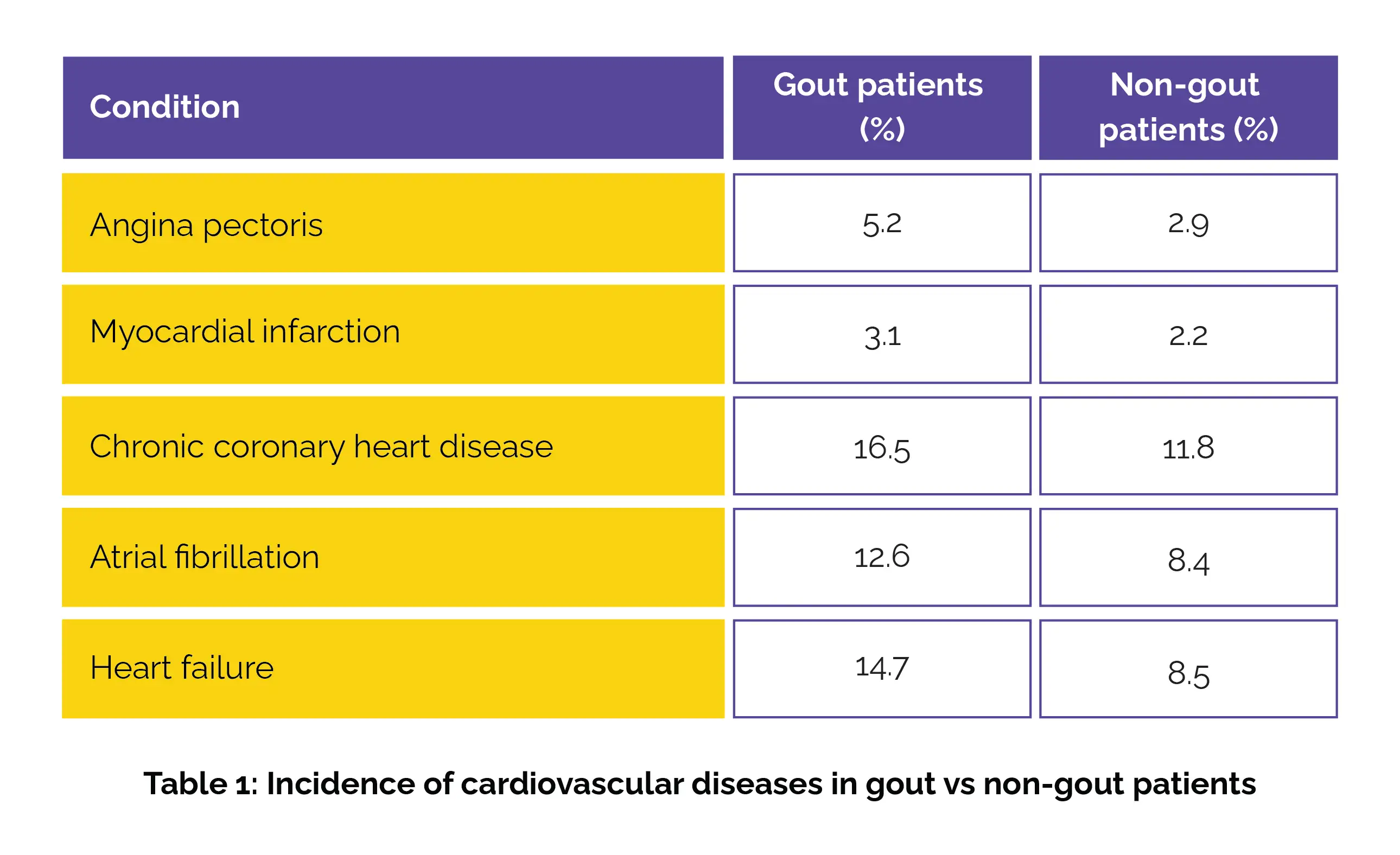
The association was stronger in male patients for all conditions except chronic coronary heart disease.
Gout may act as a risk modifier for cardiovascular diseases, possibly due to chronic inflammation. Treating gout could reduce cardiovascular risk, but further studies are needed.
Clinical Research in Cardiology
The association between gout and subsequent cardiovascular events: a retrospective cohort study with 132,000 using propensity score matching in primary care outpatients in Germany
Sedighi J et al.
Comments (0)