Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A randomized double-blind clinical trial was conducted to assess the anesthetic success rate of 2 mg (4 mg/ml) Dexamethasone added to 2% Lidocaine (with 1:80,000 Epinephrine or plain) in people with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars.
Adding 2 mg Dexamethasone improved anesthetic effectiveness of Lidocaine with Epinephrine given for inferior alveolar nerve block in people suffering from pulpitis.
A randomized double-blind clinical trial was conducted to assess the anesthetic success rate of 2 mg (4 mg/ml) Dexamethasone added to 2% Lidocaine (with 1:80,000 Epinephrine or plain) in people with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars.
A total of 124 individuals were randomly assigned to receive injections of solutions. Mandibular anesthesia was provided for the endodontic treatment of molars with irreversible pulpitis using Lidocaine 2% (plain) mixed with Dexamethasone 2 mg, Lidocaine 2% mixed with Epinephrine 1:80,000 mixed with Dexamethasone 2 mg, or Lidocaine 2% with Epinephrine 1:80,000. People with numbness of lips were subjected to electric and thermal pulp sensitivity tests 10 minutes following injection.
Subjects who responded well to the tests were labelled as "failed" anesthesia, and they were given further anesthesia. Utilizing a rubber dam, the remaining subjects had endodontic treatment. During the preparation and instrumentation (Heft-Parker visual analogue scale [HP VAS] score < 55 mm) of the endodontic access, anesthesia success was characterized as "no pain or mild/weak/faint pain". Evaluation of influence of anesthetic solutions on the maximum alteration in heart rate was also done. The success rates of anesthetics were examined using the Pearson chi-square test with 5% and 1% significance.
Anesthesia success rates for Lidocaine 2% with Epinephrine 1:80,000, Lidocaine 2% with Epinephrine 1:80,000 mixed with Dexamethasone 2 mg, and Lidocaine 2% (plain) combined with Dexamethasone 2 mg groups are depicted in Table 1:
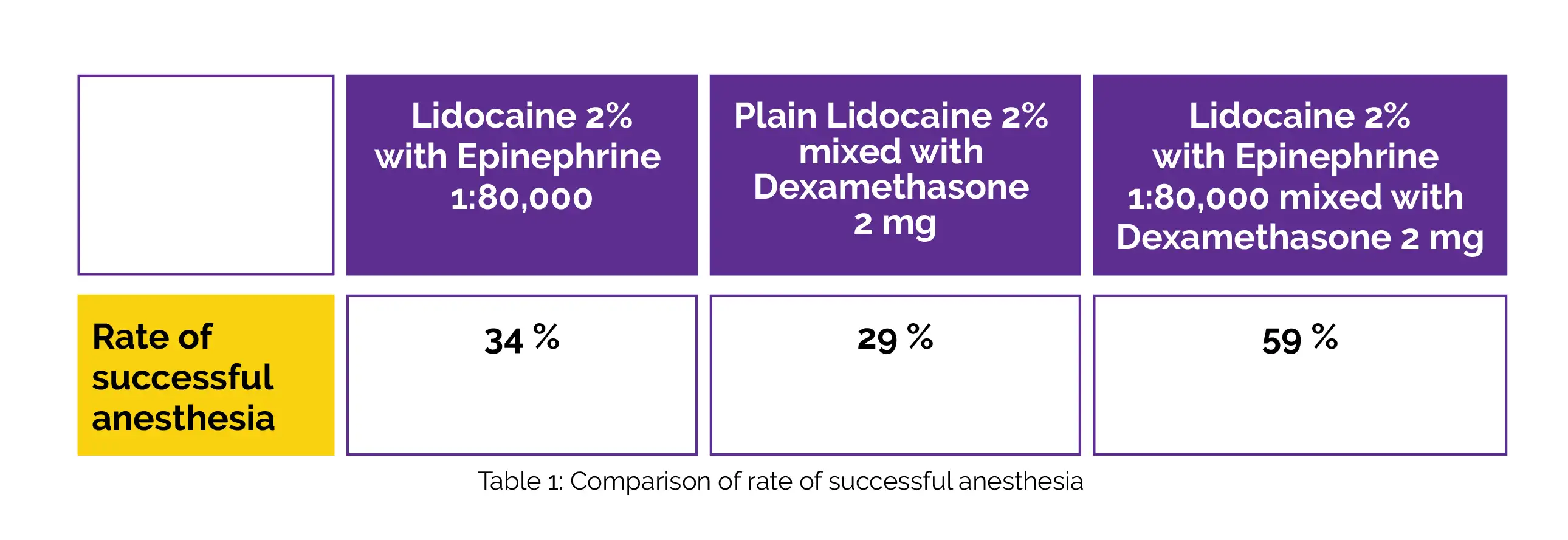
With the addition of Dexamethasone, the outcomes improved noticeably (Chi square, [χ2] = 9.07, degree of freedom [df] = 2).
When given as an inferior alveolar nerve block, Dexamethasone use as an adjunct to Lidocaine with Epinephrine was valuable for endodontic treatment of symptomatic mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis.
Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine
Addition of 2 mg Dexamethasone to improve the anesthetic efficacy of 2% Lidocaine with 1:80,000 Epinephrine administered for inferior alveolar nerve block to patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in the mandibular molars: a randomized double-blind clinical trial
Vivek Aggarwal et al.
Comments (0)