Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A single-centre, randomized controlled study aimed to examine the effects of low-dose quadruple treatment with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) on the microbiota.
When used twice daily for 10 days, low-dose Bismuth quadruple treatment can effectively eradicate H. pylori infections with reduced costs, and minimized the amount of Bismuth and antibiotics.
A single-centre, randomized controlled study aimed to examine the effects of low-dose quadruple treatment with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) on the microbiota.
Overall, 46 adult patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection were prospectively recruited. Participants received either low-dose quadruple therapy encompassing Bismuth and 20 mg Rabeprazole administered twice daily with meals for 10 days, or the same dose of Rabeprazole and antibiotics plus L. reuteri, one tablet two times a day for 27 days. Stool samples were gathered at the enrolment, at the ending, and 30-40 days post-therapy. Using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, the gut microbiota's composition was investigated.
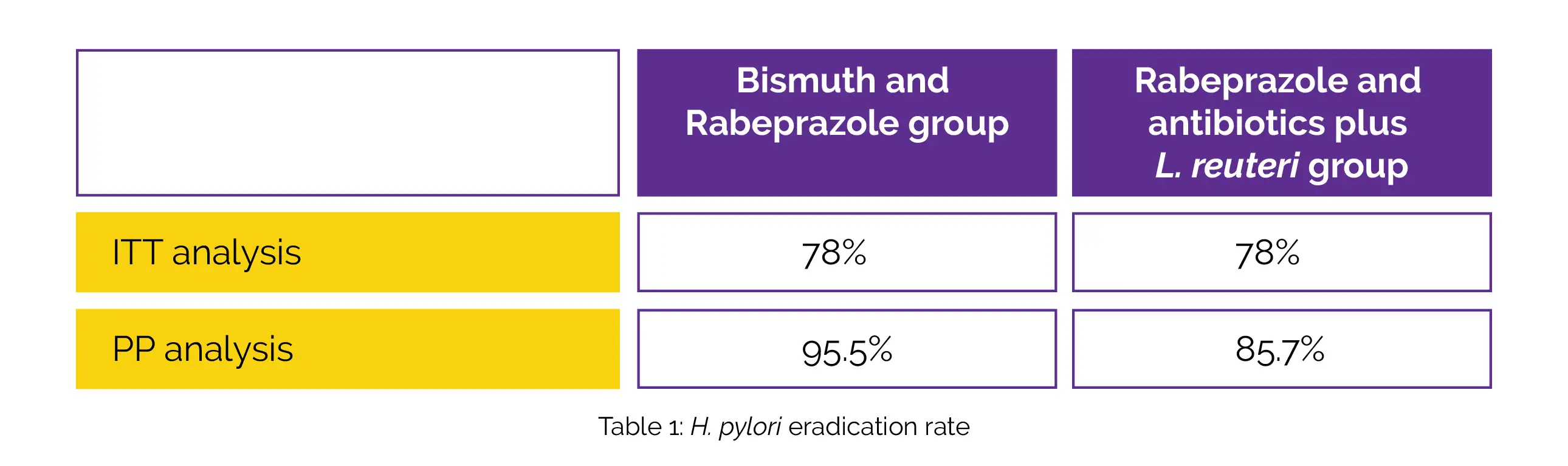
In both groups, the H. pylori elimination rate according to intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis and per protocol (PP) analysis is illustrated in Table 1:
At the end of therapy, alpha and beta diversity declined and was related to a decrease of bacterial genera useful for gut homeostasis. Both groups recovered after 30 to 40 days, indicating that the 2 regimens had a similar effect on the complexity of the bacterial community.
The use of low-dose Bismuth quadruple treatment was beneficial for H. pylori-infected patients. For subjects with contraindications to Bismuth, replacement of Bismuth with L. reuteri seems to be a promising option. However, L. reuteri was not able to substantially reverse antibiotics-triggered dysbiosis.
Nutrients
Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri
Maria Pina Dore et al.
Comments (0)