Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Diabetes mellitus, characterized by chronic high blood sugar due to insulin issues, can lead to severe complications like atherosclerosis and neuropathy. This study explored how combining Metformin with Vildagliptin compares to Metformin alone in managing Type 2 diabetes.
DPP-4 inhibitors, especially when combined with Metformin, provide effective glucose control and safety, reducing fasting and postprandial glucose levels, and minimizing hypoglycemia risk.
Diabetes mellitus, characterized by chronic high blood sugar due to insulin issues, can lead to severe complications like atherosclerosis and neuropathy. This study explored how combining Metformin with Vildagliptin compares to Metformin alone in managing Type 2 diabetes.
This 3-month longitudinal interventional study involved 100 patients with poor glycemic control on Metformin alone. They were split into two groups (50 individuals in each group): Group A continued their Metformin regimen of 500 mg or 850 mg twice daily. At the same time, Group B received a combination of Metformin 50 mg/850 mg with Vildagliptin 50 mg/500mg given twice daily.
Both treatment approaches significantly lowered fasting blood sugar (FBS) and postprandial blood sugar (PPBS) levels (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2):
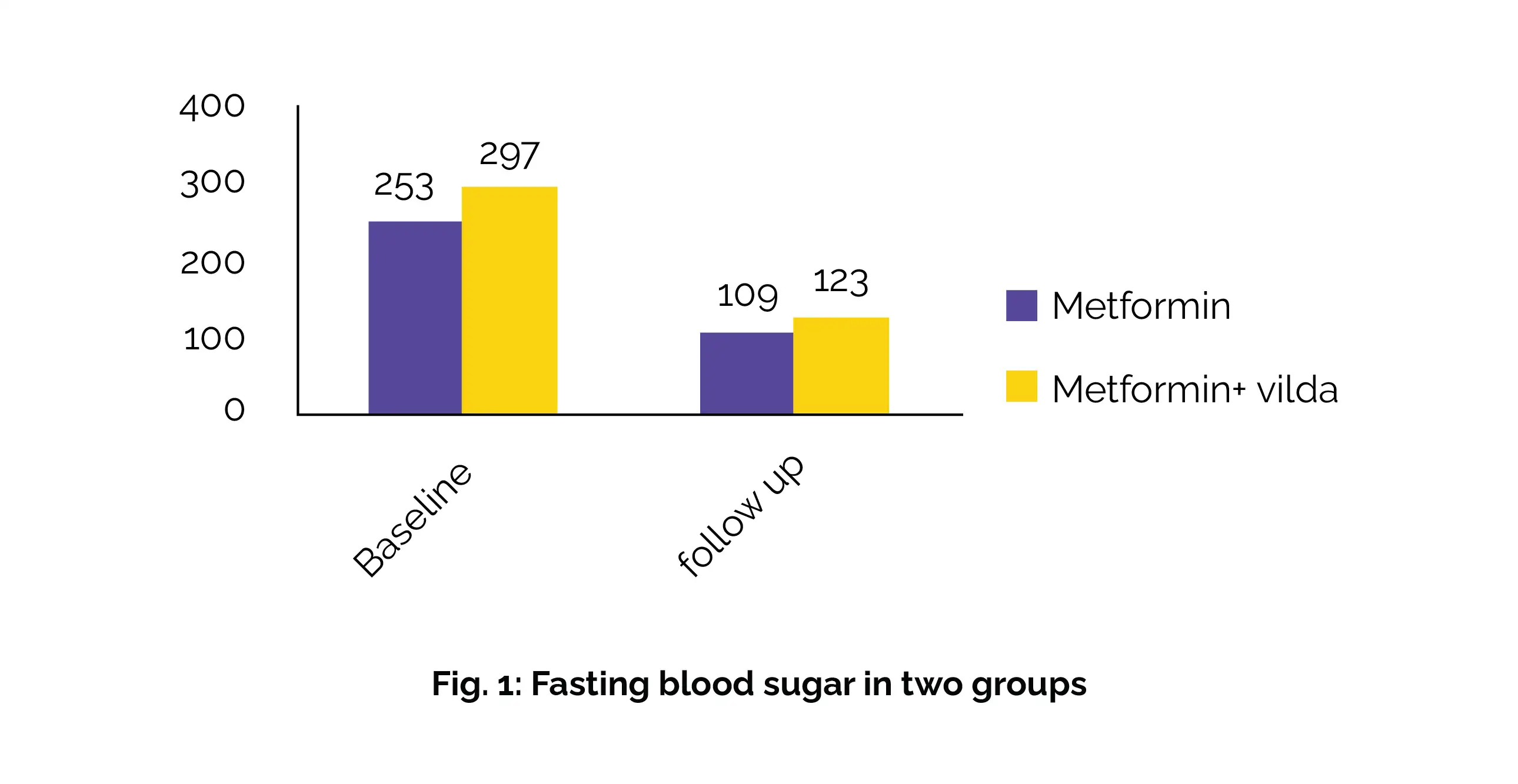
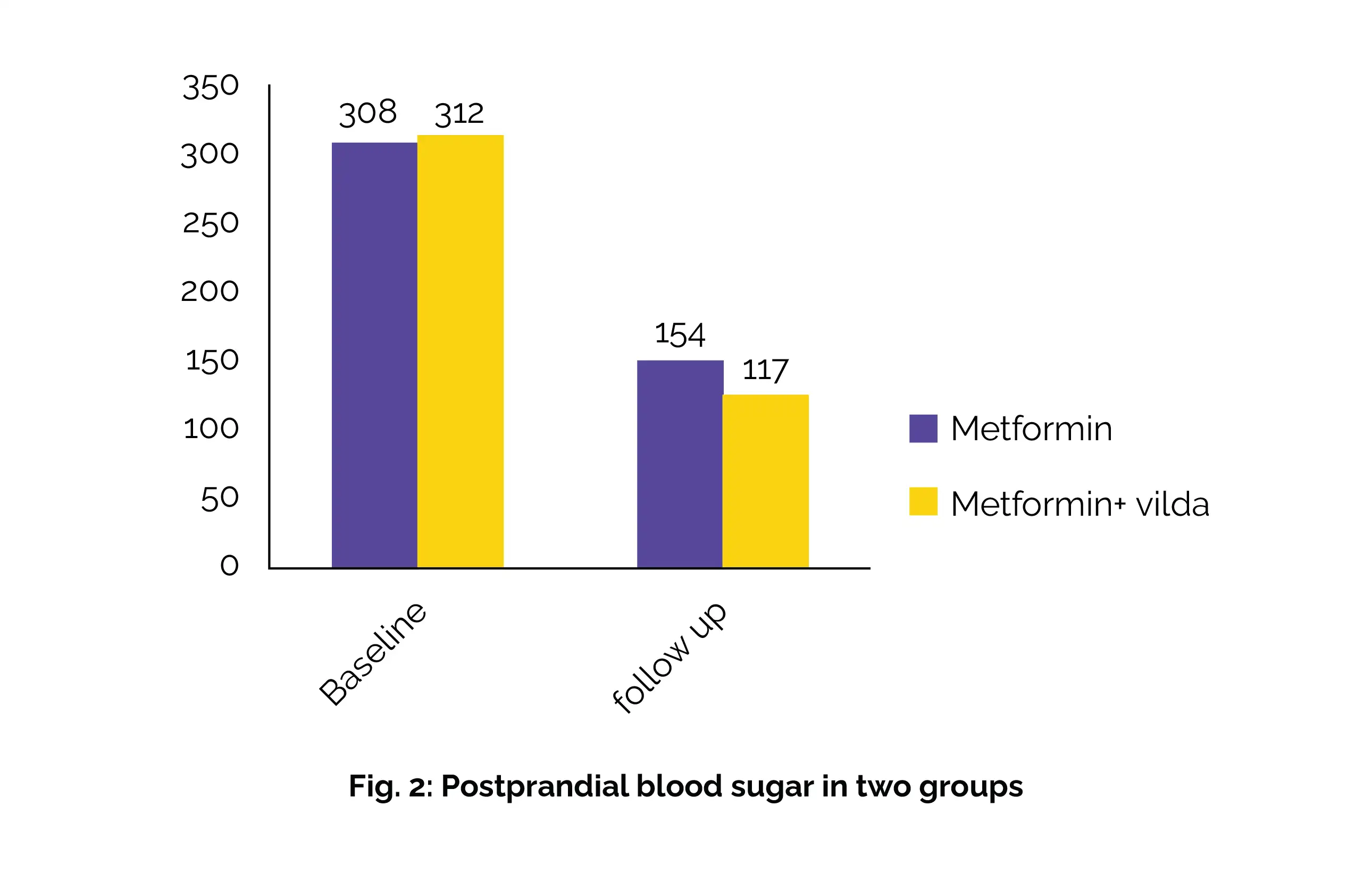
Both groups showed a significant reduction in HbA1c at 12 weeks, with no significant difference between them. Adverse effects were more common in the Metformin-only group.
The Metformin and Vildagliptin combination not only matched the efficacy of Metformin alone but also improved tolerability, reducing the risk of adverse effects.
Journal of Advanced Zoology
Comparative Analysis Of Effectiveness And Safety Between Metformin Monotherapy And The Combined Use Of Metformin With Vildagliptin In Individuals Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Heli H Amin et. al.
Comments (0)