Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


To examine the safety and effectiveness of Minocycline (tetracycline antibiotics) therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
Treatment schedules with Minocycline are effective, safe, and well-tolerated for eradicating H. pylori, offering benefits like low drug resistance and unique metabolism over tetracycline; thus, Minocycline can be a suitable alternative in clinical practice.
To examine the safety and effectiveness of Minocycline (tetracycline antibiotics) therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
A systematic search on PubMed, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Embase, SinoMed, and Wanfang Data was performed to retrieve 22 studies on H. pylori using Minocycline-containing regimens. The fixed or random effects models were utilised to investigate the eradication rates of H. pylori. Thereafter, the heterogeneity and publication bias of the studies were assessed.
Minocycline-containing regimens had high overall H. pylori eradication rates, Table 1:
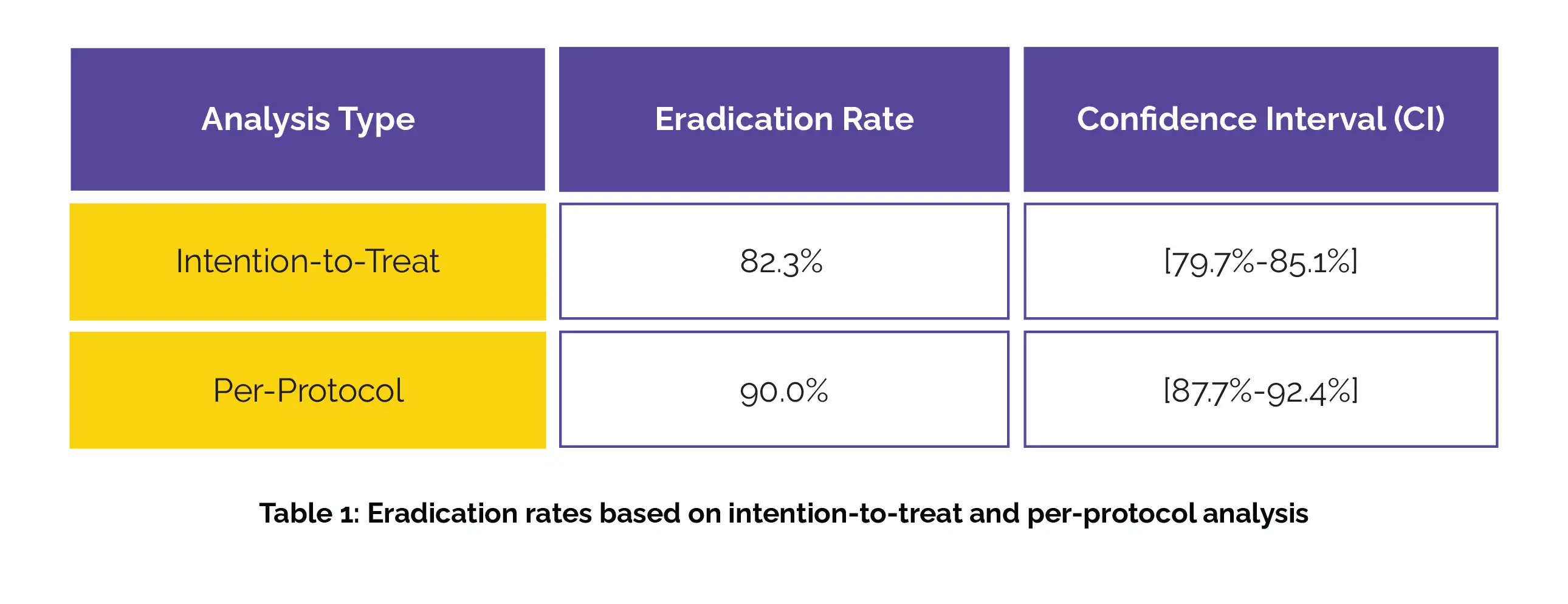
These regimens proved safe along with good compliance, with an adverse reaction rate of 36.5%. Traditional meta-analysis found that Minocycline-containing therapies were as effective as other common eradication regimens in terms of the eradication rate and frequency of adverse effects. Most adverse reactions were mild to moderate, with dizziness being notably common with the use of Minocycline.
Good efficacy, safety, and compliance were demonstrated with treatment schedules comprising Minocycline, suggesting it as a viable alternative to tetracycline for treating H. pylori-infected people.
World Journal of Gastroenterology
Minocycline in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kai Zhou et al.
Comments (0)