Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A multi-arm, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3b study was conducted to assess the effectiveness and safety of the monoclonal antibody Eptinezumab to prevent migraine in individuals with migraine and 2-4 former preventative therapy failures.
In migraineurs with two-to-four prior preventive therapy failures, Eptinezumab was safe, well-tolerated, and offered remarkable migraine preventive effects when compared to placebo.
A multi-arm, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3b study was conducted to assess the effectiveness and safety of the monoclonal antibody Eptinezumab to prevent migraine in individuals with migraine and 2-4 former preventative therapy failures.
DELIVER trial consisted of a 24-week placebo-controlled, double-blind period and a 48-week dose-blinded extension. Adults with episodic or chronic migraine who met the criteria of at least four monthly migraine days and had 2-4 prior preventative therapy failures over the preceding ten years were enrolled.
A total of 891 people were allocated at random and given at least one dosage of the study medication (safety population; 100 mg Eptinezumab [34%, n = 299], 300 mg Eptinezumab [33%, n = 294], and placebo [33%, n = 298]) using a centralized randomization system, stratified by country and baseline monthly headache days.
The alteration from baseline in the mean monthly migraine days in weeks 1-12 which was measured in the full analysis set was the primary effectiveness outcome. To study drug assignments, all study personnel and volunteers were disguised.
The placebo-controlled phase was completed by 865 patients. Table 1 illustrates the change from baseline to weeks 1–12 in mean monthly migraine days and adverse events that occurred with Eptinezumab 100 mg, with Eptinezumab 300 mg, and with placebo.
COVID-19 was the most common treatment-emergent adverse event. The incidence of severe adverse events were uncommon and included anaphylactic reaction (300 mg Eptinezumab, n = 2) and COVID-19 (100 mg Eptinezumab, n = 1 and 300 mg Eptinezumab, n = 1).
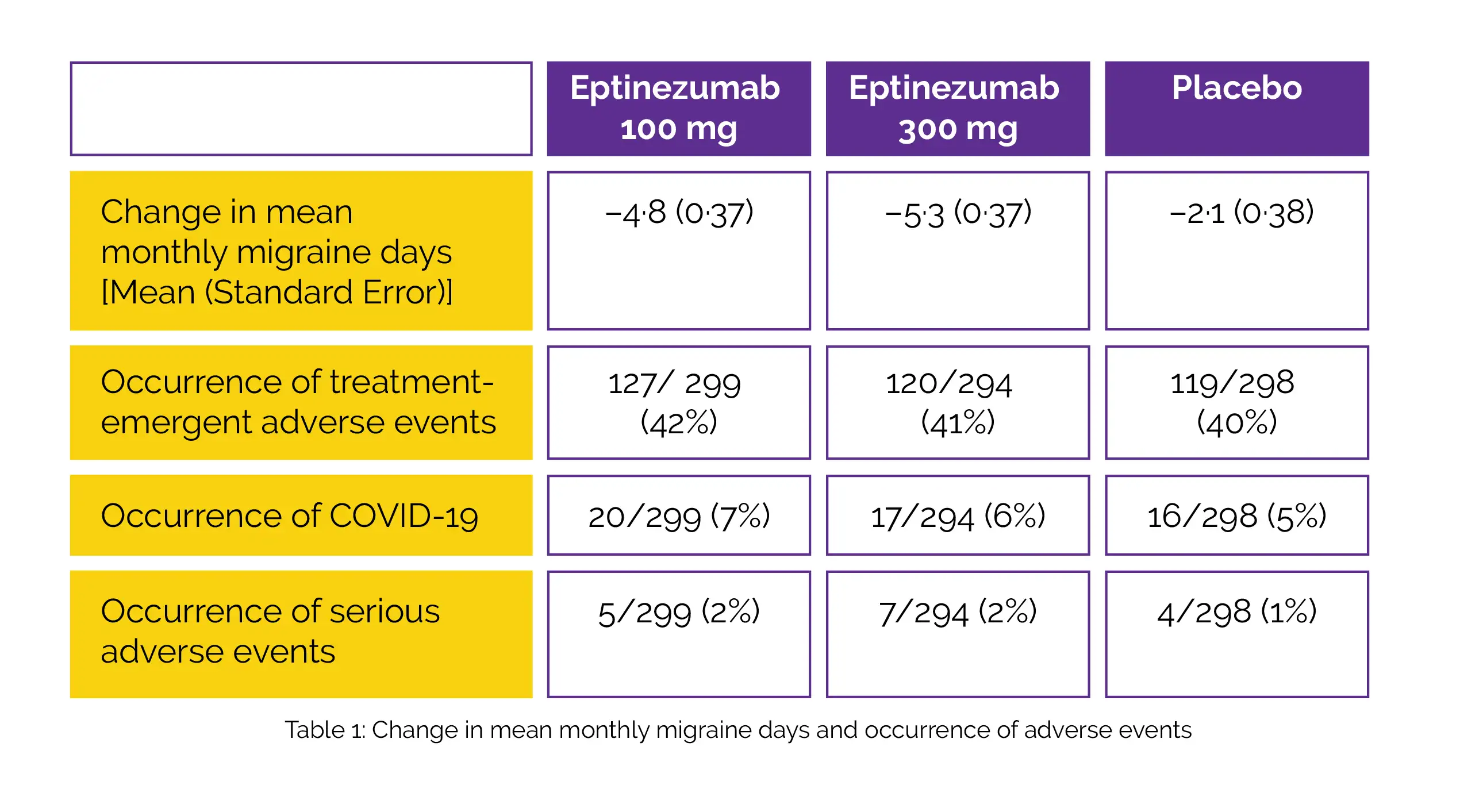
With Eptinezumab 100 mg and Eptinezumab 300 mg, there was a significant difference from placebo in the change in mean monthly migraine days from baseline.
With promising safety and tolerability profile, Eptinezumab appears to be an effective treatment option for migraine sufferers.
Lancet Neurology
Safety and efficacy of Eptinezumab for migraine prevention in patients with two-to-four previous preventive treatment failures (DELIVER): a multi-arm, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3b trial
Prof Messoud Ashina et al.
Comments (0)