Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The study aimed to evaluate and compare the levels of injection pain during inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) procedures in children, utilizing a thermomechanical device with and without audio.
In children (aged 5-10 years) undergoing dental procedures, using a thermomechanical device with an audio distraction method can effectively minimize pain encountered during inferior alveolar nerve block injection.
The study aimed to evaluate and compare the levels of injection pain during inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) procedures in children, utilizing a thermomechanical device with and without audio.
Twenty-eight children (aged 5 to 10 years) undergoing dental procedures and scheduled for IANB were included. Participants were segregated into two groups, each comprising 14 children. The study involved the use of a thermomechanical device with audio distraction in the experimental group, whereas the control group utilized the thermomechanical device without audio distraction.
IANB was administered, and the pain was subjectively evaluated through the Wong-Baker Faces Pain Rating Scale (WBFPR), while the objective pain assessment was carried out using the Faces, Legs, Activity, Consolability, Cry (FLACC) scale. Mann Whitney U test was executed for intergroup and subgroup assessment of pain on injection.
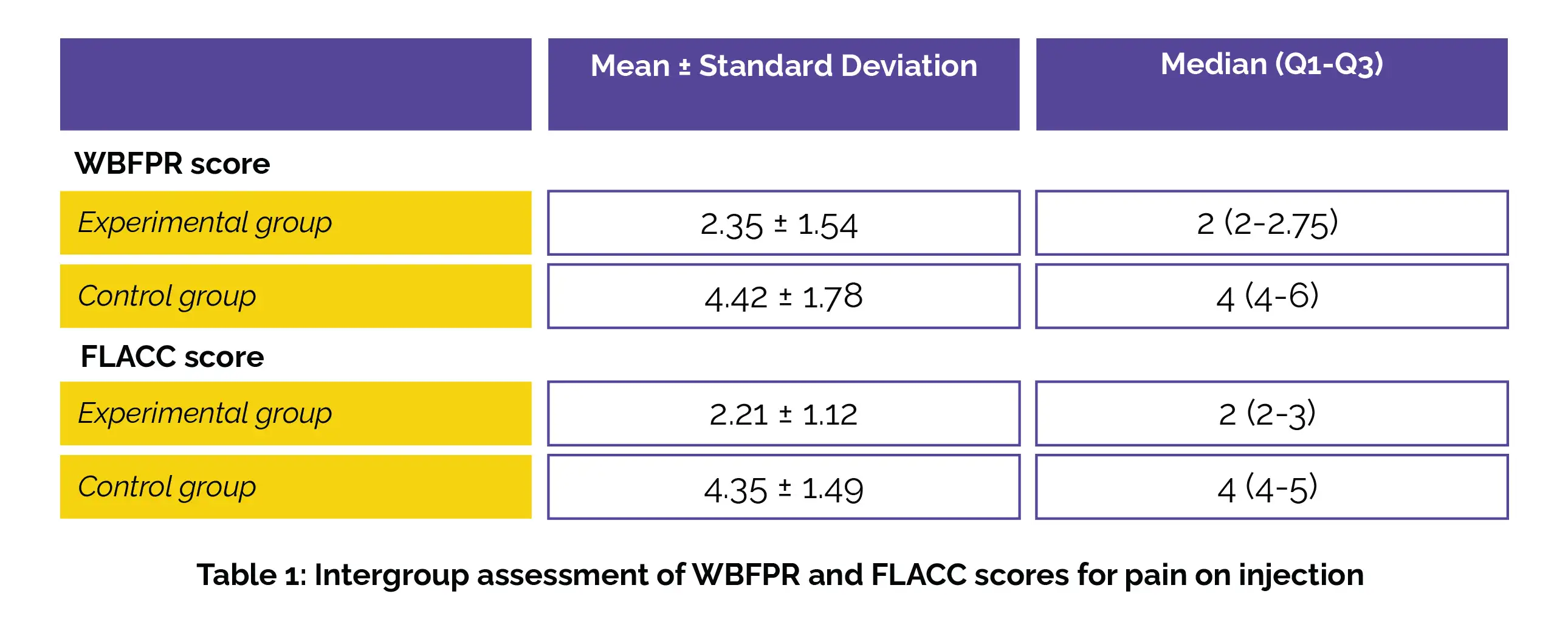
In this randomized clinical trial, a notable reduction in injection pain, as indicated by both objective and subjective assessments, was observed in the group employing the thermomechanical device with audio distraction. The intergroup analysis of pain on injection, examined using the WBFPR and FLACC scales, illustrated considerably less pain in the experimental group, as shown in Table 1:
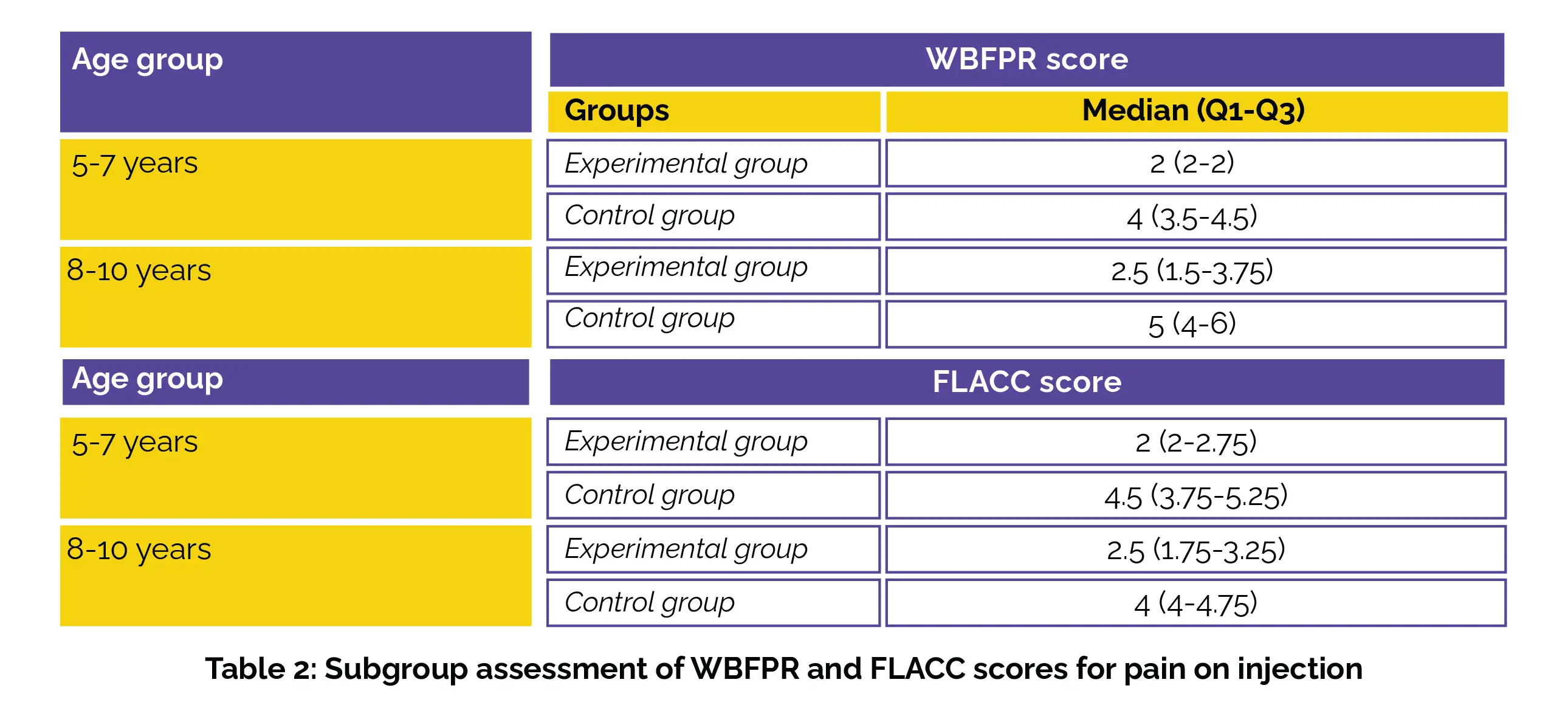
In the subgroup analysis, the mean WBFPR and FLACC scores in the experimental group were significantly lower when compared to the control group, as depicted in Table 2:
Incorporating a thermo-mechanical device along with audio distraction during IANB procedures remarkably reduced discomfort during injection in children.
Journal of Dental Anesthesia Pain Medicine
Effect of audio distraction with thermomechanical stimulation on pain perception for inferior alveolar nerve block in children: a randomized clinical trial
Devendra Nagpal et al.
Comments (0)