Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A retrospective study set out to assess the level of pain and functional recovery after treatment with various root canal flushing fluids in pulpitis patients.
The use of 3% NaClO + 0.9% saline as the root canal rinsing solution in endodontic therapy of pulpitis considerably minimized the pain level of patients after up to 6 hours of therapy, eliminated dental colonies effectively, and restored the function of temporomandibular joint.
A retrospective study set out to assess the level of pain and functional recovery after treatment with various root canal flushing fluids in pulpitis patients.
Overall, 128 individuals with pulpitis who were given root canal treatment were included in the trial. Patients were segregated into research group (n = 59) and control group (n = 69). The research group included 27 female patients and 32 male patients ranging from 27 to 41 years of age. There were 34 female subjects and 35 male subjects in the control group, aged 25-42 years old.
For root canal treatment, 3% H2O2 + 0.9% normal saline was used as root canal flushing solution in the control group while 3% NaClO + 0.9% normal saline was utilized as root canal flushing solution in the research group. Using visual analogue pain scale (VAS) and temporomandibular joint function score, pain intensity and functional recovery were assessed.
As shown in Figure 1, 3% NaClO coupled with 0.9% Sodium chloride injection efficiently decreased patients' pain levels after therapy, and the antibacterial effect was much superior to 3% H2O2 in combination with 0.9% normal saline.
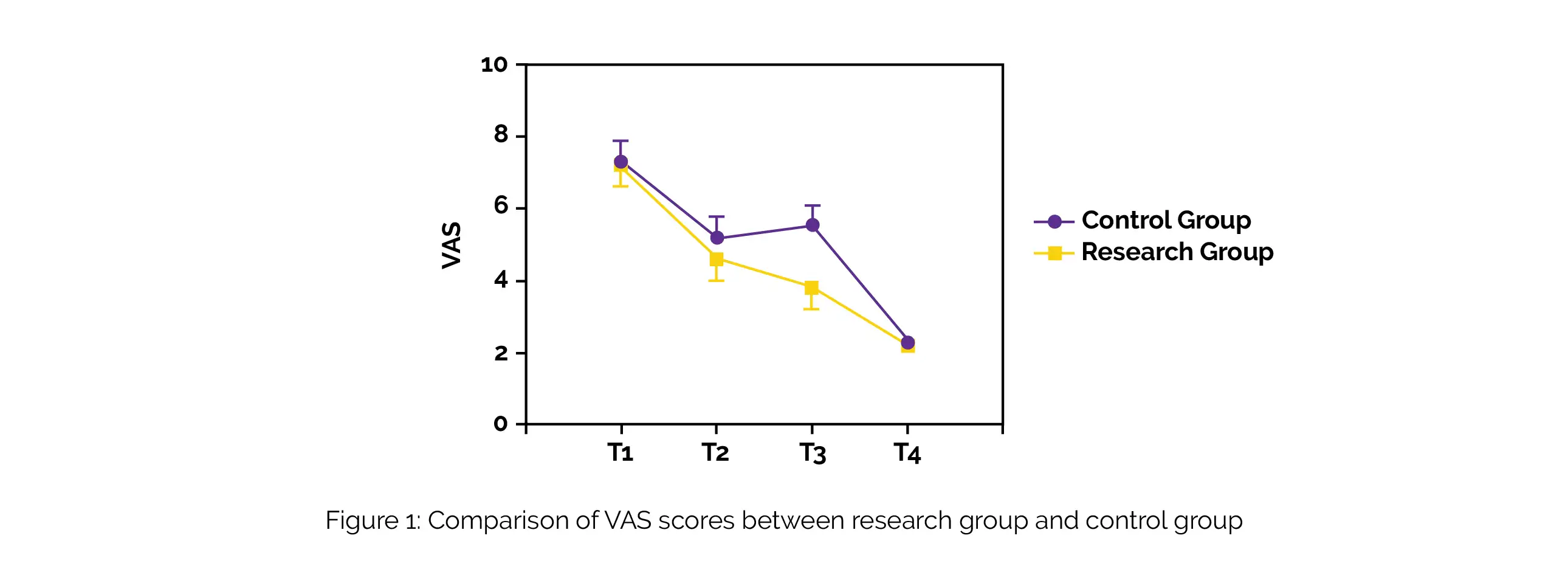
Furthermore, it effectively enhanced the temporomandibular joint function and minimized the recurrence rate, thus indicating a good clinical application value.
After treatment, pain levels in both groups were reduced, with the research group experiencing significantly reduced pain levels at the T2 and T3 stages than the control group. The temporomandibular function was improved in both groups, with the research group experiencing remarkably greater improvement contrasted to the control group.
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging
Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Pulpitis Treated with Different Root Canal Flushing Fluids Based on VAS and Temporomandibular Joint Function
Jianguo Ke et al.
Comments (0)