Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, positive-controlled clinical study was carried out to determine efficacy and safety of Polaprezinc and Rebamipide in patients with stomach ulcers.
For the treatment of gastric ulcers, Polaprezinc has comparable effectiveness and safety to Rebamipide.
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, positive-controlled clinical study was carried out to determine efficacy and safety of Polaprezinc and Rebamipide in patients with stomach ulcers.
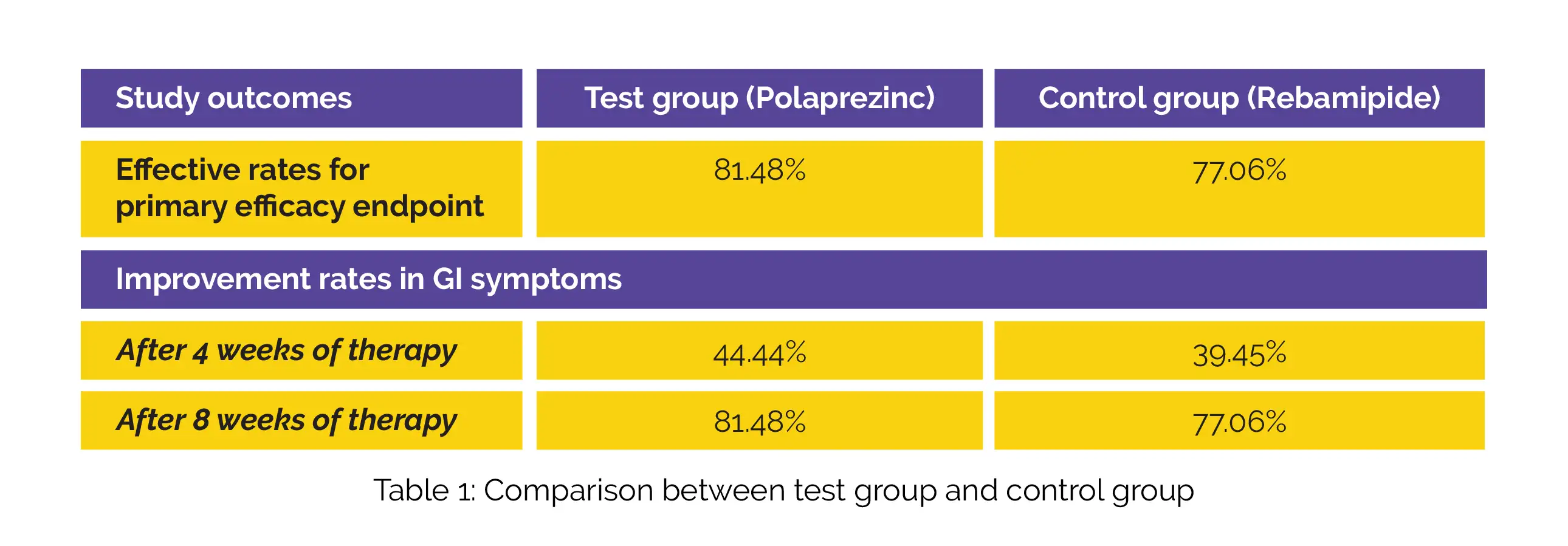
People suffering from gastric ulcers (n = 224) were prospectively recruited and split into test (n = 111) or control (n = 113) group at random. Subjects in the test group received Polaprezinc whereas the subjects in the control group were given Rebamipide tablets. Following eight weeks of therapy, a gastroscopy was used to confirm the primary outcome, which was the rate of efficient treatment. The rate of improvement in gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms after four and eight weeks of therapy served as the secondary efficacy outcome.
The two groups' fundamental traits were well balanced. For the primary efficacy outcome, the effective rates following treatment in the test and control groups, as determined by gastroscopy are shown in Table 1. Both the study groups experienced a similar rate of improvement in GI symptoms after four and eight weeks of therapy.
Comparable adverse events and reactions to study medicines were observed across both groups.
Polaprezinc granules offer the same therapeutic impact on gastric ulcers as commonly prescribed medications in clinical settings.
Medical Engineering & Physics
Efficacy and safety of Polaprezinc in the treatment of gastric ulcer: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, positive-controlled clinical trial
Wei Shen et al.
Comments (0)