Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A split-mouth, prospective randomized double-blind controlled study was carried out to determine the efficacy of Gelatamp, a bactericidal hemostatic agent on the healing of soft tissue, bleeding, and pain after the surgery of mandibular posterior teeth.
Gelatamp can be effectively used to control bleeding and restore the soft tissue without the use of prophylactic antibiotics for routine extractions of the mandibular posterior tooth.
A split-mouth, prospective randomized double-blind controlled study was carried out to determine the efficacy of Gelatamp, a bactericidal hemostatic agent on the healing of soft tissue, bleeding, and pain after the surgery of mandibular posterior teeth.
A total of 35 patients scheduled for mandibular posterior teeth extraction were divided into two groups: Experimental group with 30 patients who were given Gelatamp following the surgery, and the Control group with 30 patients. Healing of soft tissue as assessed via Landry, Turnbull, and Howley index and ease of pain via VAS score were the primary outcomes. Bleeding (Maani et al. index) and swelling (Sauza and Consone assessment) were the secondary outcomes.
Compared to the control group, the experimental group portrayed a statistically significant difference in the healing of soft tissue on the 3rd and 7th days (p ≤ 0.05), as shown in Figure 1:
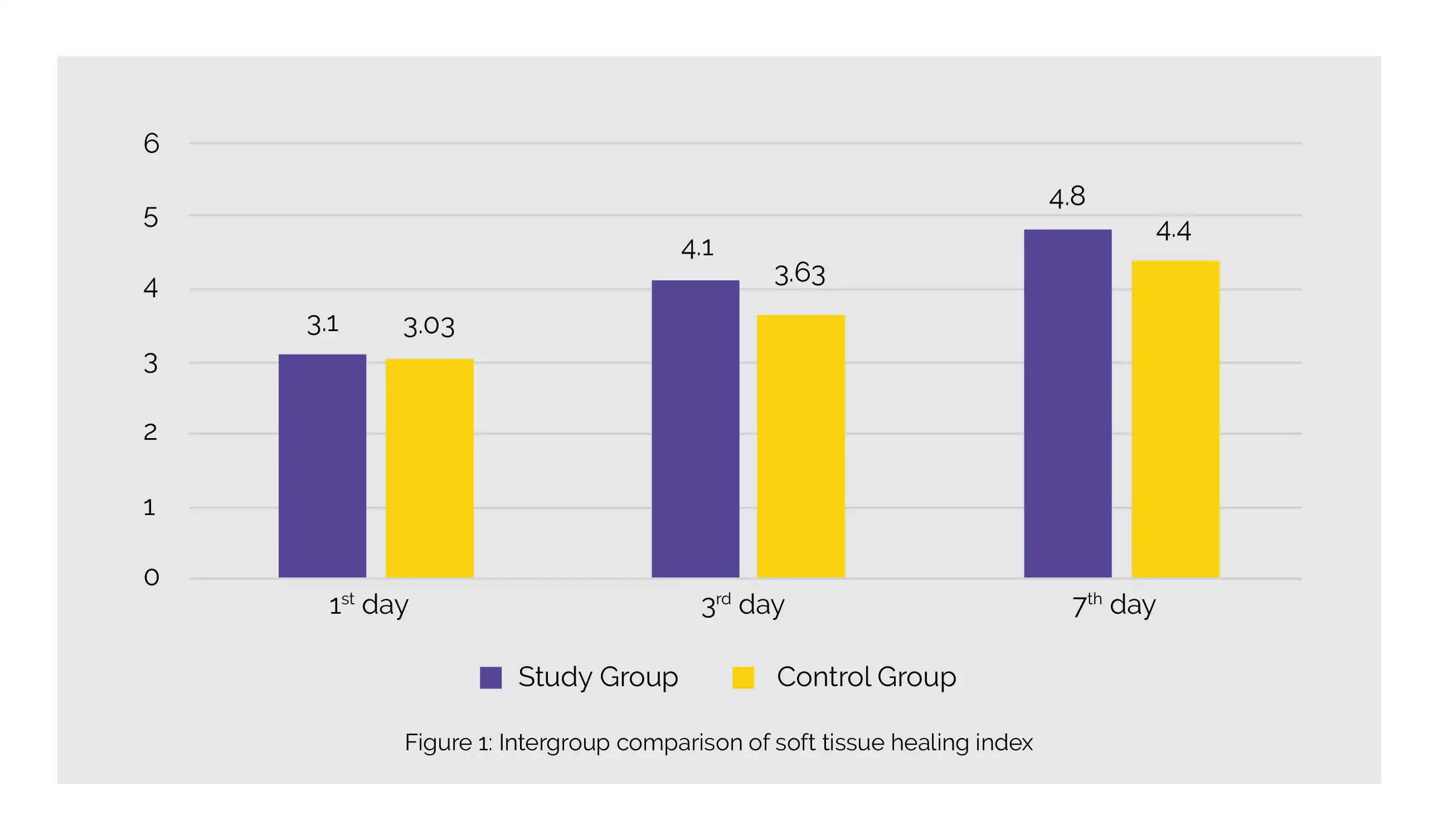
The patients in the study group had substantial differences in bleeding scores at 5 minutes, 30 minutes, and 2 hours after the extraction. Pain levels and swelling assessment had no significant difference amongst the groups.
Gelatamp can be used to reduce postoperative sequelae, for example, bleeding with improved soft tissue healing after the extractions and surgical removal of the tooth.
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research
Efficacy of gelatamp in controlling the postoperative sequelae following mandibular posterior teeth extraction - A split-mouth study
Mathew Joseph Thuruthel et al.
Comments (0)