Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A quasi-experimental clinical trial aimed to assess the efficiency of Vitamin D + Calcium supplementation, comparing it to the use of Vitamin D supplements alone, with a focus on maternal and neonatal results.
Supplementing pregnant females with Vitamin D (1000 IU) + Calcium (500 mg) during the third trimester is a beneficial intervention for mitigating maternal, neonatal, and fetal outcomes.
A quasi-experimental clinical trial aimed to assess the efficiency of Vitamin D + Calcium supplementation, comparing it to the use of Vitamin D supplements alone, with a focus on maternal and neonatal results.
Expectant mothers in their third trimester were segregated into two arms. The control arm was provided with a daily 1000 IU dose of Vitamin D, while the experimental arm was given a combined daily 1000 IU dose of Vitamin D and 500 mg of Calcium, continuing until childbirth.
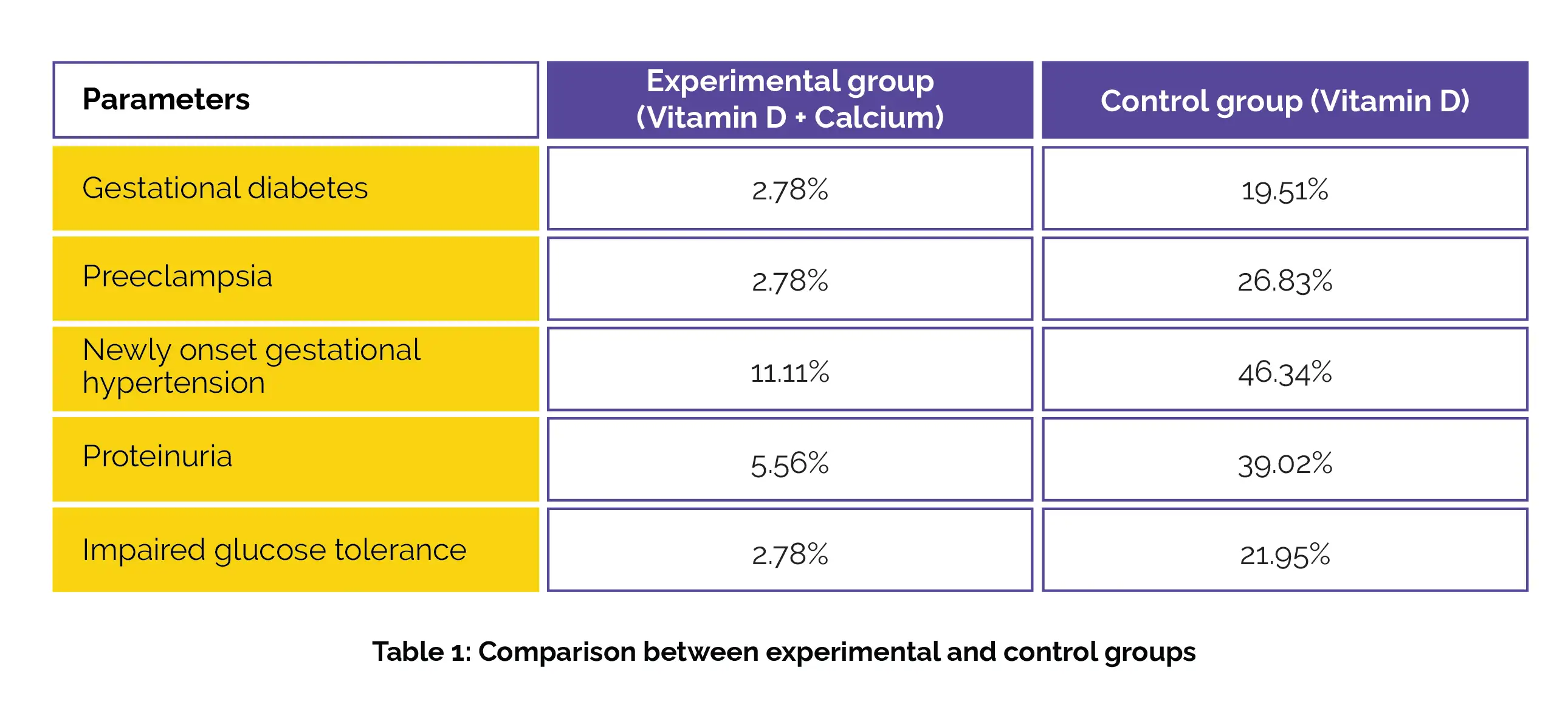
Women receiving Vitamin D and Calcium supplementation showed a reduced likelihood of developing gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, newly onset gestational hypertension, proteinuria, and impaired glucose tolerance, as shown in Table 1:
Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated lower blood pressure at the 20th and 39th weeks of gestation. Infants in the Vitamin D + Calcium arm exhibited a reduced chance of experiencing low birth weight (5.71% vs. 31.58%) and short birth length (5.71% vs. 44.74%). Furthermore, they were less prone to admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (14.29% vs. 42.11%), displayed a larger head circumference (35.00 vs. 33.63), had a longer gestational age at birth (40.0 vs. 37.56 weeks), and achieved higher APGAR scores (9.58 vs. 6.31) compared to the Vitamin D arm.
Pregnant women who were administered both Vitamin D and Calcium supplements demonstrated a reduced probability of encountering unfavorable maternal, fetal, and neonatal outcomes in comparison to those who were administered Vitamin D supplements alone.
Tzu Chi Medical Journal
https://journals.lww.com/tcmj/fulltext/9900/effectiveness_of_vitamin_d_supplementation_in.19.aspx
Effectiveness of Vitamin D supplementation in combination with calcium on risk of maternal and neonatal outcomes: A quasi-experimental clinical trial
DM Abdulah et al.
Comments (0)