Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Proton pump inhibitors do not affect recovery time or fatigue in hemodialysis patients, confirming their safety in managing these symptoms.
A study published in the ‘Journal of Clinical Medicine’ explored whether using proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) is linked to the prevalence of post-dialysis fatigue (PDF) and the time taken to recover after dialysis in patients on maintenance hemodialysis.
Maurizio Bossola and colleagues assessed 346 hemodialysis patients for their fatigue levels, including intensity, duration, and frequency of PDF on a scale from 1 to 5, along with their recovery time after dialysis (TIRD). Patients were categorized as experiencing PDF if they conveyed feeling exhausted when asked. The study also recorded the PPI use (Omeprazole, Esomeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lansoprazole, and Rabeprazole), including type, dose, and duration. The following results were observed (Table 1):
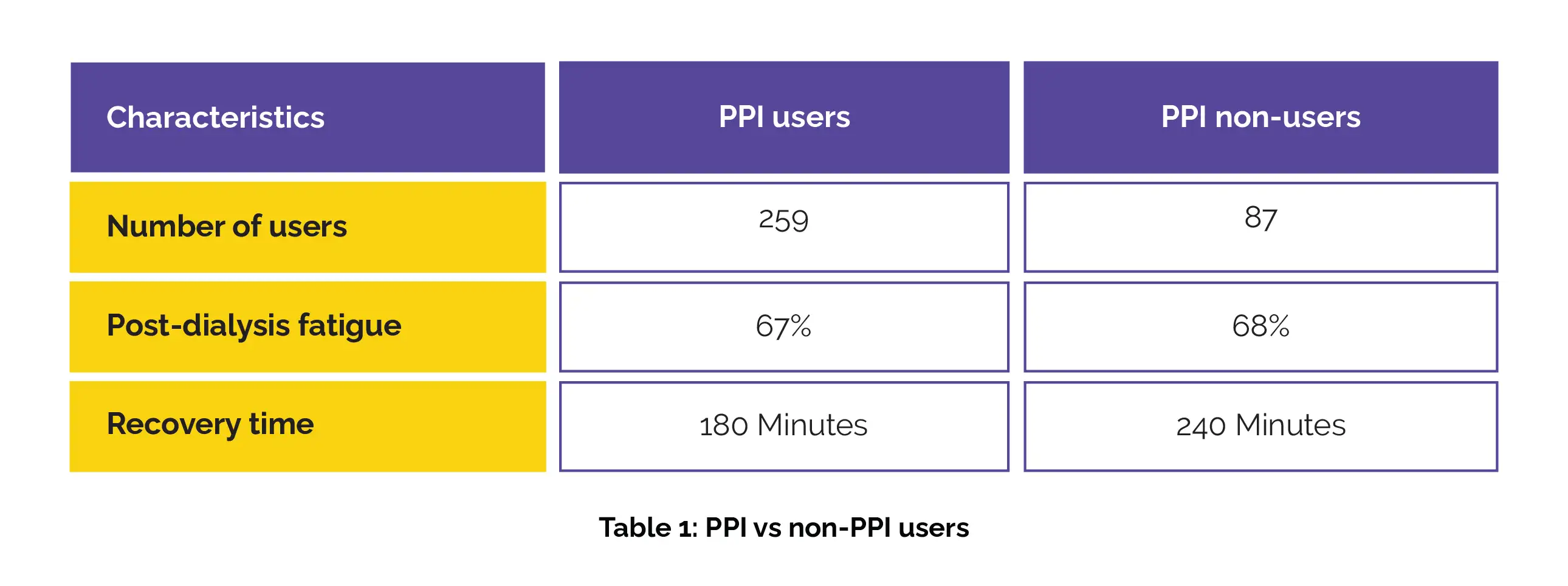
No significant changes in PDF characteristics or recovery time after dialysis were observed among different PPI types or between those using PPIs for less than 1 year versus 1 year or more.
Journal of Clinical Medicine
Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors Is Not Associated with Post-Dialysis Fatigue and Time of Recovery after Dialysis in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis
Maurizio Bossola et. Al.
Comments (0)