Змінити пароль!
Скинути пароль!


Грудне вигодовування протягом 6 місяців і більше, особливо виключно грудне вигодовування, може сприяти зниженню ризику розвитку неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки (НАЖХП) у жінок із гестаційним цукровим діабетом в анамнезі.
Згідно з результатами недавнього дослідження, грудне вигодовування, зокрема тривале і виключне, є перспективною тактикою поліпшення стану печінки у жінок з гестаційним цукровим діабетом (ГЦД) в анамнезі, яка забезпечує суттєву довгострокову користь щодо обміну речовин. Мета проспективного когортного дослідження, що включало 130 жінок протягом року після пологів, полягала у вивченні зв'язку між грудним вигодовуванням та стеатозом печінки.
Дослідники збирали інформацію про практику грудного вигодовування та вимірювали вміст жиру в печінці за допомогою контрольованих параметрів згасання (КПЗ) методом транзієнтної еластографії. Неалкогольну жирову хворобу печінки (НАЖХП) діагностували при значенні КПЗ ≥ 302 дБ/м. Жінок-добровольців розділили на 3 групи залежно від тривалості та інтенсивності грудного вигодовування:
Отримані результати виявилися вражаючими. У групі 3 у жінок з найбільш тривалим грудним вигодовуванням спостерігалося найнижчий вміст жиру в печінці. Поширеність НАЖХП у групі 3 була значно нижчою, ніж у групах 1 та 2 (таблиця 1).
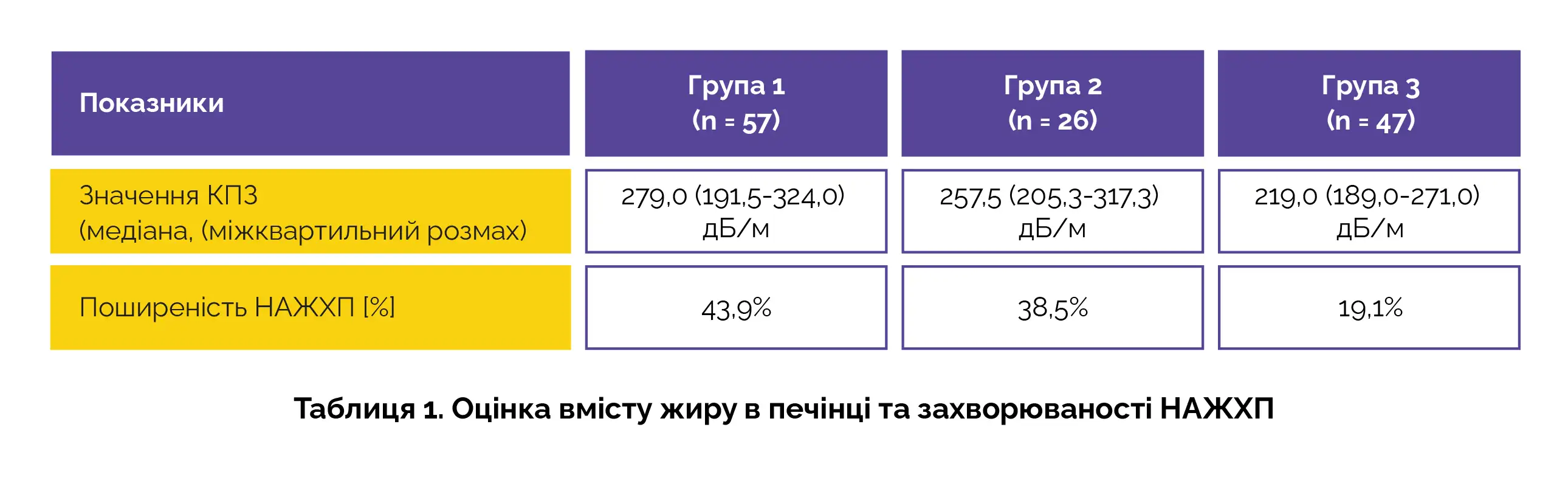
Статистична значущість цих результатів робить їх ще більш примітними: згідно з результатами багатофакторного аналізу, грудне вигодовування протягом 6 місяців і більше, особливо винятково грудне вигодовування протягом перших 6 місяців мінімізує ризик розвитку НАЖХП (скориговане відношення шансів 0,34).
У цьому дослідженні був розглянутий післяпологовий період, що часто не береться до уваги, і було встановлено, що грудне вигодовування не тільки сприяє розвитку немовлят, але і може забезпечити довгострокову користь для здоров'я матерів, що робить його важливим фактором у боротьбі з довгостроковими наслідками ГЦД. Результати цього дослідження є вагомими підставами для розгляду можливості продовження грудного вигодовування як тактики підтримки здоров'я печінки у жінок, які стикаються з труднощами післяпологового відновлення.
International Breastfeeding Journal
Relationship between breastfeeding and hepatic steatosis in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus
Supatsri Sethasine та співавт.
Коментарі (0)