Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This randomized controlled trial aimed to investigate effectiveness of vonoprazan based dual therapy vs proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based therapy for elimination of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
Vonoprazan based dual treatment offers an acceptable H. pylori elimination rate with reduced adverse events.
This randomized controlled trial aimed to investigate effectiveness of vonoprazan based dual therapy vs proton pump inhibitor (PPI) based therapy for elimination of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
The study included 192 H. pylori-infected people (age 18-75 years) and randomized them into (i) Group-A (n=96): Received 1 gm amoxicillin capsule; 500 mg clarithromycin tablet; 20 mg omeprazole capsule twice daily for two weeks, (ii) Group-B (n=96): Received 1 gm amoxicillin capsule; 20 mg vonoprazan tablet twice daily for two weeks.
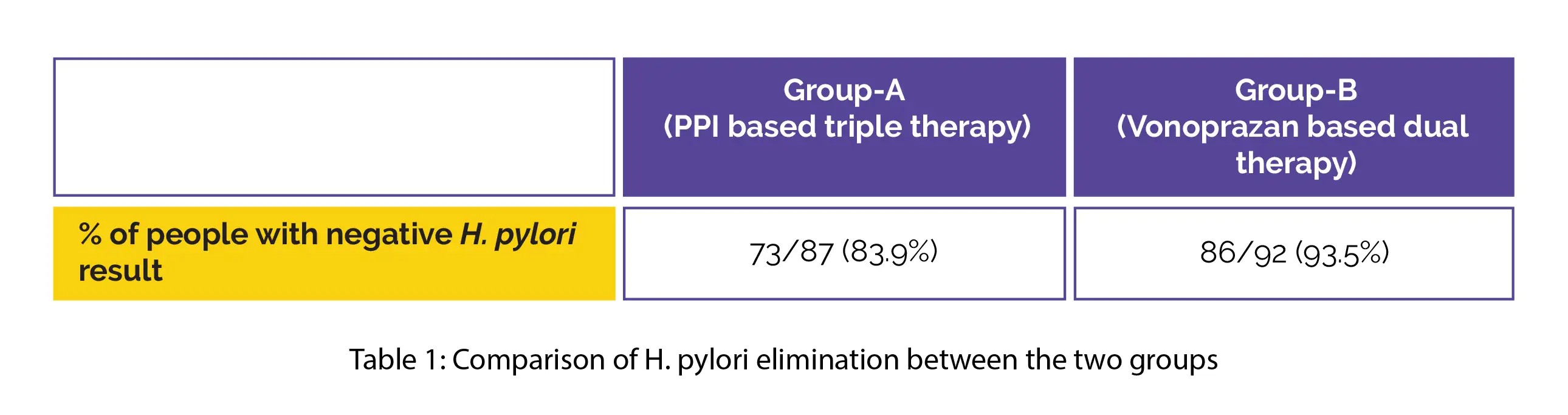
Confirmation of H. pylori elimination was done by stool H. pylori antigen test four weeks following therapy completion. The assessment was carried out on 87 people in Group A and 92 people in Group B.
The percentage of people with negative H. pylori results after treatment, is shown in Table 1:
Substantially greater frequencies of adverse events were noted in Group A in comparison with Group B in bloating and nausea/vomiting.
Compared to conventional PPI based triple therapy, the vonoprazan based dual therapy was more likely to eliminate H. pylori. Thus, vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy appears to be a promising new first-line therapy for H. pylori infection.
Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences
Comparison of Vonoprazan and Amoxicillin Dual Therapy with Standard Triple Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor for Helicobacter Pylori eradication: A Randomized Control Trial
Bader Faiyaz Zuberi et al.
Comments (0)