Змінити пароль!
Скинути пароль!


Ціль полягала у вивченні ефективності різних неінвазивних методів терапії (НІМТ) для лікування хронічного тінітусу у дорослих.
Звукова та когнітивно-поведінкова терапія може бути ефективна в лікуванні хронічного тінітусу за рахунок заглушення шуму у вухах, зменшення гіперчутливості до звуків та покращення загальної якості життя пацієнтів внаслідок полегшення психологічного стресу.
Ціль полягала у вивченні ефективності різних неінвазивних методів терапії (НІМТ) для лікування хронічного тінітусу у дорослих.
Були вивчені бази даних PubMed, Embase та Cochrane. Оцінку різних НІМТ, таких як терапія прийняття та відповідальності, когнітивно-поведінкова терапія, звукотерапія, транскраніальна магнітна стимуляція, електростимуляційна терапія, віртуальна реальність, терапія перенавчання при тінітусі, психотерапія та плацебо, проводили відповідно до рекомендацій для систематичних оглядів та мета-аналізу» (PRISMA).
Для оцінки результатів використовували опитувальник з оцінки впливу тінітусу (THI), опитувальник тінітусу (TQ), госпітальну шкалу тривоги та депресії (HADS), індекс тяжкості безсоння (ISI) та візуальну аналогову шкалу (для оцінки гучності (VAS-L) та психологічного стресу (VAS-D)). Для статистичного аналізу проведення мережевого метааналізу (СМА) використовували програмне забезпечення Stata 14.0.
У цей систематичний огляд та метааналіз включили 22 рандомізованих контрольованих дослідження, що включали загалом 2354 пацієнти. При оцінці різних шкал ефекти терапії розрізнялися (таблиця 1).
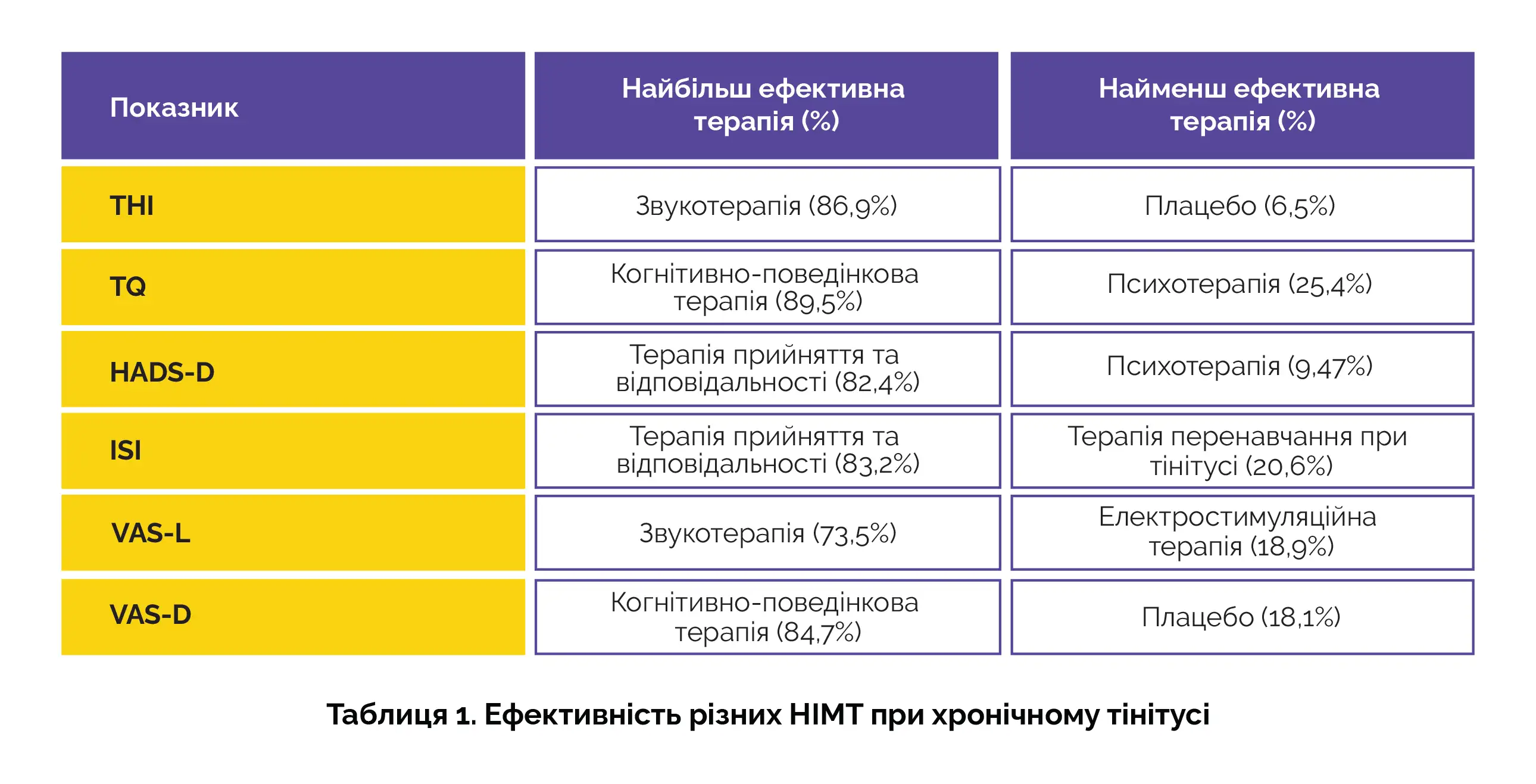
Звукова терапія (звукотерапія) та когнітивно-поведінкова терапія були ефективними у дорослих пацієнтів з хронічним тінітусом.
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology
http://www.bjorl.org/en-non-invasive-treatments-improve-patient-outcomes-articulo-S1808869424000533
Non-invasive treatments improve patient outcomes in chronic tinnitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Tingting Lu і співавт.
Коментарі (0)