Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


This study examined neuromuscular electrical stimulation and Ibuprofen for pain management in femoral head necrosis (also known as avascular necrosis of the femoral head).
Combination of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and Ibuprofen improves pain, quality of life, and hip function in femoral head necrosis-affected people, while also lowering the levels of osteopontin, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, and leptin.
This study examined neuromuscular electrical stimulation and Ibuprofen for pain management in femoral head necrosis (also known as avascular necrosis of the femoral head).
Overall, 60 femoral head necrosis-affected patients (aged between 18 and 85 years) who were hospitalized between October 2020 and October 2021 were split into 2 groups. The observation group (n=30) received neuromuscular electrical stimulation along with Ibuprofen. On the other hand, the control group (n=30) received oral Ibuprofen sustained-release capsules. Both groups underwent a 4-week therapy course.
Key outcomes such as therapeutic efficacy, Harris Hip Score, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) pain score, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) hip imaging stage, 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36) health survey score, and levels of serum plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), leptin, and osteopontin were compared before and after treatment.
As opposed to the control group, the observation group exhibited a markedly better overall response rate. Post-treatment Harris Hip Scores were quite higher in both groups, with the observation group illustrating greater improvement. In this retrospective study, the VAS scores dropped in both groups, with a more drastic decline in the observation group (Figure 1).
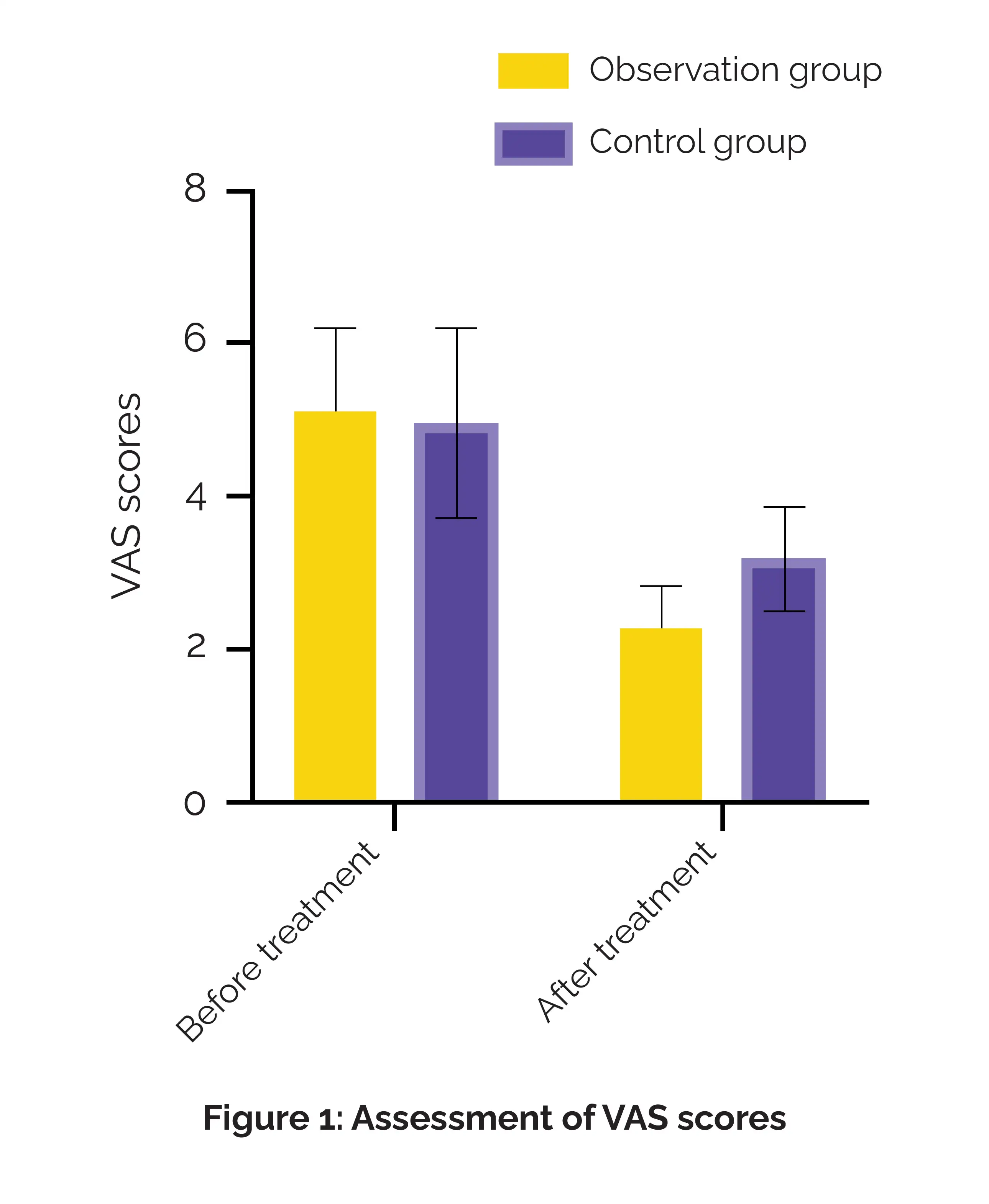
More patients in both groups had a 0-I MRI hip imaging stage post-treatment, with the observation group depicting a greater improvement. SF-36 scores elevated in both groups, with a larger improvement witnessed in the observation group. In both groups, the levels of PAI-1, leptin, and osteopontin in the serum dropped. The observation group showed more pronounced reductions.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation + Ibuprofen markedly improved pain management, quality of life, and hip function in femoral head necrosis sufferers. Additionally, it also reduced the levels of PAI-1, leptin, and osteopontin.
American Journal of Translational Research
Combination of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and ibuprofen to reduce pain in femoral head necrosis
Boyu Liu et al.
Comments (0)