Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


A comparative interventional study was conducted to assess the effect of Vitamin B-12 in alleviating chronic low backache.
Intramuscular injections of Vitamin B-12 can be safely administered with minimal to no side effects and can serve as an adjunct treatment for chronic low back pain.
A comparative interventional study was conducted to assess the effect of Vitamin B-12 in alleviating chronic low backache.
Overall, 496 subjects were recruited and segregated into Group I (n=256) and Group II (n=240). Volunteers in Group I received treatment with Vitamin B-12, while people in Group II were not given Vitamin B-12. Evaluation of the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores was done prior to the treatment.
Individuals in Group II received non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and calcium supplements for a month, whereas Group I received Vitamin B-12 (500 mcg) injections intramuscularly on alternate days for 1 month, in addition to NSAIDs and calcium supplements.
The mean VAS and ODI scores before and after treatment are illustrated in Table 1:
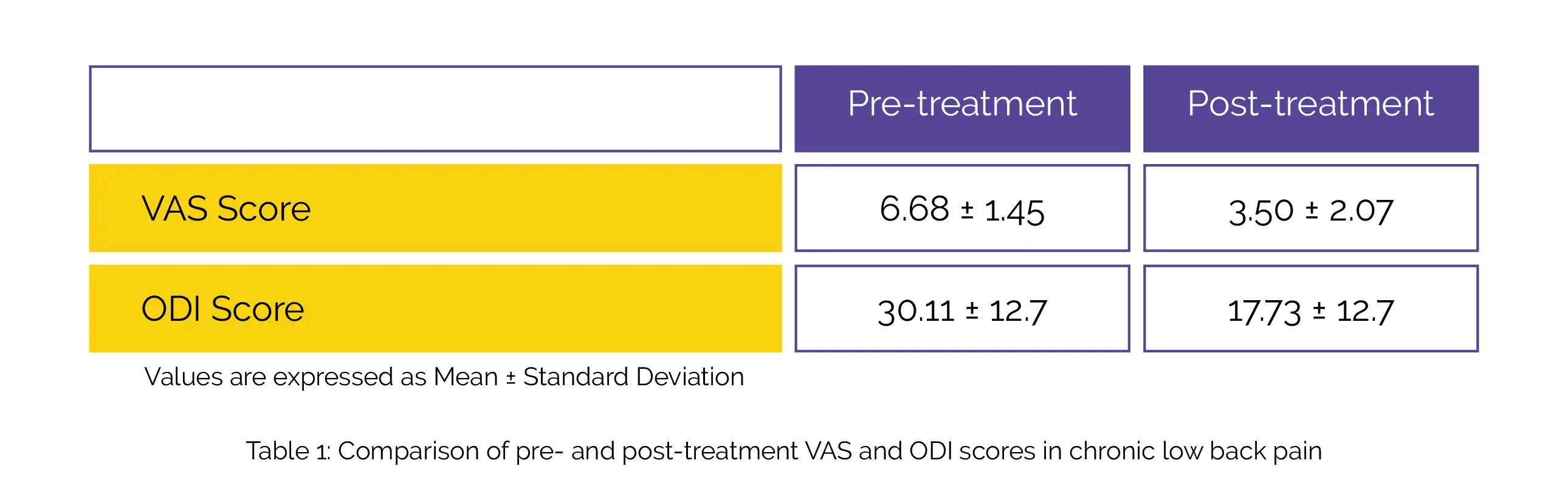
This indicates a significant reduction in VAS and ODI scores following the administration of Vitamin B-12. None of the volunteers reported injection site complications.
The concurrent use of Vitamin B-12 demonstrated a superior effect in alleviating symptoms of chronic backache compared to those without Vitamin B-12 treatment.
International Journal of Endorsing Health Science Research
Role of Vitamin B-12 in chronic low backache: A comparative study
Syed Danish Ali et al.
Comments (0)